A New Type of Motor: Pneumatic Step Motor
- PMID: 21528106
- PMCID: PMC3082205
- DOI: 10.1109/TMECH.2006.886258
A New Type of Motor: Pneumatic Step Motor
Abstract
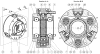
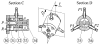
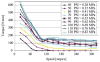
This paper presents a new type of pneumatic motor, a pneumatic step motor (PneuStep). Directional rotary motion of discrete displacement is achieved by sequentially pressurizing the three ports of the motor. Pulsed pressure waves are generated by a remote pneumatic distributor. The motor assembly includes a motor, gearhead, and incremental position encoder in a compact, central bore construction. A special electronic driver is used to control the new motor with electric stepper indexers and standard motion control cards. The motor accepts open-loop step operation as well as closed-loop control with position feedback from the enclosed sensor. A special control feature is implemented to adapt classic control algorithms to the new motor, and is experimentally validated. The speed performance of the motor degrades with the length of the pneumatic hoses between the distributor and motor. Experimental results are presented to reveal this behavior and set the expectation level. Nevertheless, the stepper achieves easily controllable precise motion unlike other pneumatic motors. The motor was designed to be compatible with magnetic resonance medical imaging equipment, for actuating an image-guided intervention robot, for medical applications. For this reason, the motors were entirely made of nonmagnetic and dielectric materials such as plastics, ceramics, and rubbers. Encoding was performed with fiber optics, so that the motors are electricity free, exclusively using pressure and light. PneuStep is readily applicable to other pneumatic or hydraulic precision-motion applications.
Figures








Similar articles
-
"MRI Stealth" robot for prostate interventions.Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2007;16(4):241-8. doi: 10.1080/13645700701520735. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2007. PMID: 17763098 Free PMC article.
-
High Speed Pneumatic Stepper Motor for MRI Applications.Ann Biomed Eng. 2019 Mar;47(3):826-835. doi: 10.1007/s10439-018-02174-0. Epub 2018 Dec 14. Ann Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 30552529
-
An MR-conditional high-torque pneumatic stepper motor for MRI-guided and robot-assisted intervention.Ann Biomed Eng. 2014 Sep;42(9):1823-33. doi: 10.1007/s10439-014-1049-x. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Ann Biomed Eng. 2014. PMID: 24957635 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Additive Manufacture, and Control of a Pneumatic, MR-Compatible Needle Driver.IEEE Trans Robot. 2016 Feb;32(1):138-149. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2504981. Epub 2016 Jan 19. IEEE Trans Robot. 2016. PMID: 31105476 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Control of a Pneumatic Motor for MR-conditional Robotic Applications.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2017 Dec;22(6):2780-2789. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2767906. Epub 2017 Nov 1. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2017. PMID: 31105420 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MRI Robots for Needle-Based Interventions: Systems and Technology.Ann Biomed Eng. 2018 Oct;46(10):1479-1497. doi: 10.1007/s10439-018-2075-x. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Ann Biomed Eng. 2018. PMID: 29922958 Free PMC article.
-
A 10-mm MR-Conditional Unidirectional Pneumatic Stepper Motor.IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015 Apr;20(2):782-788. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2014.2305839. IEEE ASME Trans Mechatron. 2015. PMID: 25419104 Free PMC article.
-
Design, development, and evaluation of an MRI-guided SMA spring-actuated neurosurgical robot.Int J Rob Res. 2015 Jul;34(8):1147-1163. doi: 10.1177/0278364915579069. Epub 2015 May 18. Int J Rob Res. 2015. PMID: 26622075 Free PMC article.
-
MR-Conditional Actuations: A Review.Ann Biomed Eng. 2020 Dec;48(12):2707-2733. doi: 10.1007/s10439-020-02597-8. Epub 2020 Aug 27. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 32856179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MR conditional prostate intervention systems and actuations review.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2023 Jan;237(1):18-34. doi: 10.1177/09544119221136169. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2023. PMID: 36458323 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choi HS, Han CS, Lee KY, Lee SH. Development of hybrid robot for construction works with pneumatic actuator. Autom Construc. 2005;14:452–459.
-
- Hagglund T. A friction compensator for pneumatic control valves. J Process Control. 2002;12:897–904.
-
- Bendov D, Salcudean SE. A force-controlled pneumatic actuator. IEEE Trans Robot Autom. 1995 Dec;11(6):906–911.
-
- Butefisch S, Seidemann V, Buttgenbach S. Novel micro-pneumatic actuator for MEMS. Sens Actuators A, Phys. 2002;97–98:638–645.
-
- vanVarseveld RB, Bone GM. Accurate position control of a pneumatic actuator using on/off solenoid valves. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatronics. 1997 Sep;2(3):195–204.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
