Murine immune responses to a Plasmodium vivax-derived chimeric recombinant protein expressed in Brassica napus
- PMID: 21529346
- PMCID: PMC3098821
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-106
Murine immune responses to a Plasmodium vivax-derived chimeric recombinant protein expressed in Brassica napus
Abstract
Background: To develop a plant-based vaccine against Plasmodium vivax, two P. vivax candidate proteins were chosen. First, the merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1), a major asexual blood stage antigen that is currently considered a strong vaccine candidate. Second, the circumsporozoite protein (CSP), a component of sporozoites that contains a B-cell epitope.
Methods: A synthetic chimeric recombinant 516 bp gene encoding containing PvMSP-1, a Pro-Gly linker motif, and PvCSP was synthesized; the gene, named MLC, encoded a total of 172 amino acids. The recombinant gene was modified with regard to codon usage to optimize gene expression in Brassica napus. The Ti plasmid inducible gene transfer system was used for MLC chimeric recombinant gene expression in B. napus. Gene expression was confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), beta-glucuronidase reporter gene (GUS) assay, and Western blot.
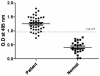
Results: The MLC chimeric recombinant protein expressed in B. napus had a molecular weight of approximately 25 kDa. It exhibited a clinical sensitivity of 84.21% (n=38) and a clinical specificity of 100% (n=24) as assessed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Oral immunization of BALB/c mice with MLC chimeric recombinant protein successfully induced antigen-specific IgG1 production. Additionally, the Th1-related cytokines IL-12 (p40), TNF, and IFN-γ were significantly increased in the spleens of the BALB/c mice.
Conclusions: The chimeric MLC recombinant protein produced in B. napus has potential as both as an antigen for diagnosis and as a valuable vaccine candidate for oral immunization against vivax malaria.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Trials for the co-expression of the merozoite surface protein-1 and circumsporozoite protein genes of Plasmodium vivax.Exp Parasitol. 2011 Nov;129(3):227-33. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2011.08.014. Epub 2011 Aug 28. Exp Parasitol. 2011. PMID: 21907198
-
Generation, characterization and immunogenicity of a novel chimeric recombinant protein based on Plasmodium vivax AMA-1 and MSP119.Vaccine. 2017 Apr 25;35(18):2463-2472. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.03.023. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28341111
-
Immune responses elicited by co-immunization of Plasmodium vivax and P. falciparum MSP-1 using prime-boost immunization strategies.Parasite Immunol. 2011 Nov;33(11):594-608. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2011.01331.x. Parasite Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21883290
-
Immunogenicity of Plasmodium vivax combination subunit vaccine formulated with human compatible adjuvants in mice.Vaccine. 2007 Jul 9;25(28):5166-74. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.04.080. Epub 2007 May 21. Vaccine. 2007. PMID: 17544179
-
Production of recombinant proteins from protozoan parasites.Trends Parasitol. 2010 May;26(5):244-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2010.02.004. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Trends Parasitol. 2010. PMID: 20189877 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Edible plants for oral delivery of biopharmaceuticals.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Jan;83(1):71-81. doi: 10.1111/bcp.12949. Epub 2016 May 9. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27037892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of the international plant science community to the fight against infectious diseases in humans-part 2: Affordable drugs in edible plants for endemic and re-emerging diseases.Plant Biotechnol J. 2021 Oct;19(10):1921-1936. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13658. Epub 2021 Jul 19. Plant Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34181810 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant Platforms for Efficient Heterologous Protein Production.Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2021;26(4):546-567. doi: 10.1007/s12257-020-0374-1. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng. 2021. PMID: 34393545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphism of the parasite lactate dehydrogenase gene from Plasmodium vivax Korean isolates.Malar J. 2013 May 21;12:166. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-12-166. Malar J. 2013. PMID: 23688062 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic variation of aldolase from Korean isolates of Plasmodium vivax and its usefulness in serodiagnosis.Malar J. 2012 May 8;11:159. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-159. Malar J. 2012. PMID: 22569198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendis K, Sina BJ, Marchesini P, Cater R. The neglected burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:97–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

