Genotypic profile of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and clinical features of infection in humans, Thailand
- PMID: 21529392
- PMCID: PMC3321758
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1705.100754
Genotypic profile of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 and clinical features of infection in humans, Thailand
Abstract
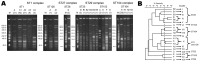
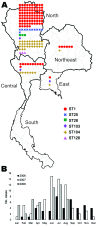
To examine associations between clinical features of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 infections in humans in Thailand and genotypic profiles of isolates, we conducted a retrospective study during 2006-2008. Of 165 patients for whom bacterial cultures of blood, cerebrospinal fluid, or both were positive for S. suis serotype 2, the major multilocus sequence types (STs) found were ST1 (62.4%) and ST104 (25.5%); the latter is unique to Thailand. Clinical features were examined for 158 patients. Infections were sporadic; case-fatality rate for adults was 9.5%, primarily in northern Thailand. Disease incidence peaked during the rainy season. Disease was classified as meningitis (58.9%) or nonmeningitis (41.1%, and included sepsis [35.4%] and others [5.7%]). Although ST1 strains were significantly associated with the meningitis category (p<0.0001), ST104 strains were significantly associated with the nonmeningitis category (p<0.0001). The ST1 and ST104 strains are capable of causing sepsis, but only the ST1 strains commonly cause meningitis.
Figures
References
-
- Fongcom A, Pruksakorn S, Mongkol R, Tharavichitkul P, Yoonim N. Streptococcus suis infection in northern Thailand. J Med Assoc Thai. 2001;84:1502–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
