Analysis of CaM-kinase signaling in cells
- PMID: 21529938
- PMCID: PMC3236032
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2011.02.007
Analysis of CaM-kinase signaling in cells
Abstract
A change in intracellular free calcium is a common signaling mechanism that modulates a wide array of physiological processes in most cells. Responses to increased intracellular Ca(2+) are often mediated by the ubiquitous protein calmodulin (CaM) that upon binding Ca(2+) can interact with and alter the functionality of numerous proteins including a family of protein kinases referred to as CaM-kinases (CaMKs). Of particular interest are multifunctional CaMKs, such as CaMKI, CaMKII, CaMKIV and CaMKK, that can phosphorylate multiple downstream targets. This review will outline several protocols we have used to identify which members and/or isoforms of this CaMK family mediate specific cellular responses with a focus on studies in neurons. Many previous studies have relied on a single approach such as pharmacological inhibitors or transfected dominant-negative kinase constructs. Since each of these protocols has its limitations, that will be discussed, we emphasize the necessity to use multiple, independent approaches in mapping out cellular signaling pathways.
Published by Elsevier India Pvt Ltd.
Figures
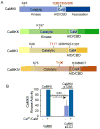
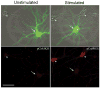

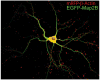
References
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. Signal transduction. The calcium entry pas de deux. Science. 2000;287:1604–5. - PubMed
-
- Higley MJ, Sabatini BL. Calcium signaling in dendrites and spines: practical and functional considerations. Neuron. 2008;59:902–13. - PubMed
-
- Gaertner TR, Kolodziej SJ, Wang D, Kobayashi R, Koomen JM, Stoops JK, Waxham MN. Comparative analyses of the three-dimensional structures and enzymatic properties of alpha, beta, gamma and delta isoforms of Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:12484–94. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg OS, Deindl S, Comolli LR, Hoelz A, Downing KH, Nairn AC, Kuriyan J. Oligomerization states of the association domain and the holoenyzme of Ca2+/CaM kinase II. FEBS J. 2006;273:682–94. - PubMed
-
- Haribabu B, Hook SS, Selbert MA, Goldstein EG, Tomhave ED, Edelman AM, Snyderman R, Means AR. Human calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase I: cDNA cloning, domain structure and activation by phosphorylation at threonine-177 by calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase I kinase. EMBO J. 1995;14:3679–86. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

