Pathogenesis of acute kidney injury: foundation for clinical practice
- PMID: 21530035
- PMCID: PMC3144267
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.02.385
Pathogenesis of acute kidney injury: foundation for clinical practice
Abstract
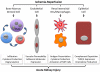
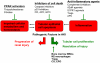
The pathogenesis of acute kidney injury (AKI) is complex, involving such factors as vasoconstriction, leukostasis, vascular congestion, cell death, and abnormal immune modulators and growth factors. Many targeted clinical therapies have failed, are inconclusive, or have yet to be tested. Given the complexity of the pathogenesis of AKI, it may be naive to expect that one therapeutic intervention would have success. Some examples of detrimental processes that can be blocked in preclinical models to improve kidney function and survival are apoptotic cell death in tubular epithelial cells, complement-mediated immune system activation, and impairment of cellular homeostasis and metabolism. Modalities with the potential to decrease morbidity and mortality in patients with AKI include vasodilators, growth factors, anti-inflammatory agents, and cell-based therapies. Pharmacologic agents that target these diverse pathways are being used clinically for other indications. Using combinatorial approaches in future clinical trials may improve our ability to prevent and treat AKI.
Copyright © 2011 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Sutton TA, Fisher CJ, Molitoris BA. Microvascular endothelial injury and dysfunction during ischemic acute renal failure. Kidney Int. 2002;62:1539–1549. - PubMed
-
- Okusa MD. The inflammatory cascade in acute ischemic renal failure. Nephron. 2002 Feb;90:133–138. - PubMed
-
- Thadhani R, Pascual M, Bonventre JV. Acute renal failure. NEnglJMed. 1996;334:1448–1460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 DK083185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK085259/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32DK083185/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK62324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK072922/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R41 DK058413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK088967/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK56223/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK083406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK088967/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK062324/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK58413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK093841/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44 DK058413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

