Nucleophilic radiosynthesis of 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-galactose from Talose triflate and biodistribution in a porcine model
- PMID: 21531284
- PMCID: PMC3131089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.11.006
Nucleophilic radiosynthesis of 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-galactose from Talose triflate and biodistribution in a porcine model
Abstract
Introduction: The galactose analogue 2-[(18)F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-galactose (FDGal) is a promising positron emission tomography (PET) tracer for studies of regional differences in liver metabolic function and for clinical evaluation of patients with liver cirrhosis and patients undergoing treatment of liver diseases. However, there is an unmet need for routine production of FDGal from readily available starting material. In this study, we present the preparation of FDGal with high radiochemical purity and in amounts sufficient for clinical investigations from commercially available Talose triflate (1,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-2-O-trifluoromethanesulfonyl-β-D-talopyranose). In addition, the biodistribution of FDGal in the pig is presented.
Methods: FDGal was prepared by nucleophilic fluorination of Talose triflate followed by basic hydrolysis. The entire synthesis was performed using the GE TRACERlab MX 2-[(18)F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG) synthesizer and existing methods for quality control of FDG were applied. Biodistribution of FDGal was studied by successive whole-body PET recordings of two anaesthetized 37-kg pigs.
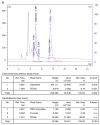
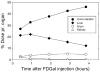
Results: Up to 3.7 GBq sterile, pyrogen-free and no-carrier-added FDGal was produced with a radiochemical yield of 3.8±1.2% and a radiochemical purity of 98±1% (42 productions; yield is decay corrected). The adopted quality control methods for FDG were directly applicable for FDGal. Biodistribution studies in the pig revealed the liver and the urinary bladder as critical organs in terms of radiation dose.
Conclusion: Commercially available Talose triflate is a suitable starting material for routine productions of FDGal. The presented radiosynthesis and quality control methods allow for the production of pure, no-carrier-added FDGal in sufficient amounts for clinical PET-investigations of the liver.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


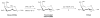
References
-
- Caputto R, Leloir LF, Trucco RE, Cardini CE, Paladini AC. The enzymatic transformation of galactose into glucose derivatives. J Biol Chem. 1949;179:497–8. - PubMed
-
- Holden HM, Rayment I, Thoden JB. Structure and function of enzymes of the Leloir pathway for galactose metabolism. J Biol Chem. 2003;45:43885–8. - PubMed
-
- Keiding S, Johansen S, Winkler K, Tønnesen K, Tygstrup N. Michaelis-Menten kinetics of galactose elimination by the isolated perfused pig liver. Am J Physiol. 1976;230:1302–13. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda H, Matsuzawa T, Tada M, Takahashi T, Ishiwata K, Yamada K, et al. 2-Deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-galactose: a new tracer for the measurement of galactose metabolism in the liver by positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med. 1986;11:444–8. - PubMed
-
- Grün B, Berger U, Oberdorfer F, Hull WE, Ostertag H, Friedrich E, et al. Metabolism and actions of 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-D-galactose in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1990;190:11–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

