Maximal brain size remains an important predictor of cognition in old age, independent of current brain pathology
- PMID: 21531482
- PMCID: PMC3177982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.03.017
Maximal brain size remains an important predictor of cognition in old age, independent of current brain pathology
Abstract
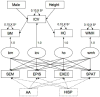
There is growing interest in the influence of early-life development on clinical manifestations of late-life diseases. Latent variable modeling was used to investigate how maximal brain volume (measured by intracranial volume [ICV]) and current brain volumes uniquely contribute to domain-specific cognitive performance in a group of 401 cognitively and ethnically diverse older adults. Individual effects of volumetric magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measures including ICV were examined as predictors of episodic memory, semantic memory, spatial ability, and executive function. Total brain matter volume related to all cognitive domains; hippocampal volume was associated primarily with episodic memory; white matter hyperintensity volume was related to executive function and episodic memory. Maximal brain size as measured by ICV was related to semantic memory, executive function, and spatial ability independent of current brain volumes (ps < 0.01). Relationships between magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) variables and cognition did not differ substantially across groups defined by ethnicity, gender, and with minor exceptions, clinical diagnosis. Results suggest maximal brain development and measures of brain injury/atrophy jointly contribute to cognitive function in older people.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors of this paper have any actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1987.
-
- Bentler PM. Comparative fit indices in structural models. Psychol Bul. 1990;107:238–246. - PubMed
-
- Bentler PM. EQS for Windows User’s Guide. Encino, CA: Multivariate Software; 1995.
-
- Borenstein Graves A, Mortimer JA, Bowen JD, McCormick WC, McCurry SM, Schellenberg GD, Larson EB. Head circumference and incident Alzheimer’s disease: modification by apolipoprotein E. Neurology. 2001;57:1453–1460. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

