Restoration of G1 chemo/radioresistance and double-strand-break repair proficiency by wild-type but not endonuclease-deficient Artemis
- PMID: 21531702
- PMCID: PMC3159448
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr257
Restoration of G1 chemo/radioresistance and double-strand-break repair proficiency by wild-type but not endonuclease-deficient Artemis
Abstract
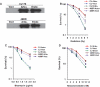
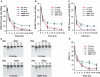
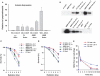
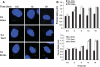
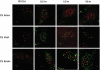
Deficiency in Artemis is associated with lack of V(D)J recombination, sensitivity to radiation and radiomimetic drugs, and failure to repair a subset of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). Artemis harbors an endonuclease activity that trims both 5'- and 3'-ends of DSBs. To examine whether endonucleolytic trimming of terminally blocked DSBs by Artemis is a biologically relevant function, Artemis-deficient fibroblasts were stably complemented with either wild-type Artemis or an endonuclease-deficient D165N mutant. Wild-type Artemis completely restored resistance to γ-rays, bleomycin and neocarzinostatin, and also restored DSB-repair proficiency in G0/G1 phase as measured by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and repair focus resolution. In contrast, cells expressing the D165N mutant, even at very high levels, remained as chemo/radiosensitive and repair deficient as the parental cells, as evidenced by persistent γ-H2AX, 53BP1 and Mre11 foci that slowly increased in size and ultimately became juxtaposed with promyelocytic leukemia protein nuclear bodies. In normal fibroblasts, overexpression of wild-type Artemis increased radioresistance, while D165N overexpression conferred partial repair deficiency following high-dose radiation. Restoration of chemo/radioresistance by wild-type, but not D165N Artemis suggests that the lack of endonucleolytic trimming of DNA ends is the principal cause of sensitivity to double-strand cleaving agents in Artemis-deficient cells.
Figures
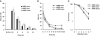
References
-
- Moshous D, Callebaut I, de Chasseval R, Corneo B, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Le Deist F, Tezcan I, Sanal O, Bertrand Y, Philippe N, et al. Artemis, a novel DNA double-strand break repair/V(D)J recombination protein, is mutated in human severe combined immune deficiency. Cell. 2001;105:177–186. - PubMed
-
- Ma Y, Pannicke U, Schwarz K, Lieber MR. Hairpin opening and overhang processing by an Artemis/DNA- dependent protein kinase complex in nonhomologous end joining and V(D)J recombination. Cell. 2002;108:781–794. - PubMed
-
- Riballo E, Kuhne M, Rief N, Doherty A, Smith GC, Recio MJ, Reis C, Dahm K, Fricke A, Krempler A, et al. A pathway of double-strand break rejoining dependent upon ATM, artemis, and proteins locating to γ-H2AX foci. Mol. Cell. 2004;16:715–724. - PubMed

