WD repeat-containing protein 5, a ubiquitously expressed histone methyltransferase adaptor protein, regulates smooth muscle cell-selective gene activation through interaction with pituitary homeobox 2
- PMID: 21531708
- PMCID: PMC3122240
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.233098
WD repeat-containing protein 5, a ubiquitously expressed histone methyltransferase adaptor protein, regulates smooth muscle cell-selective gene activation through interaction with pituitary homeobox 2
Abstract
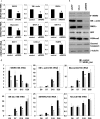
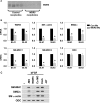
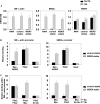
WD repeat-containing protein 5 (WDR5) is a common component of mammalian mixed lineage leukemia methyltransferase family members and is important for histone H3 lysine 4 methylation (H3K4me), which has been implicated in control of activation of cell lineage genes during embryogenesis. However, WDR5 has not been considered to play a specific regulatory role in epigenetic programming of cell lineage because it is ubiquitously expressed. Previous work from our laboratory showed the appearance of histone H3K4me within smooth muscle cell (SMC)-marker gene promoters during the early stages of development of SMC from multipotential embryonic cells but did not elucidate the underlying mechanisms that mediate SMC-specific and locus-selective H3K4me. Results presented herein show that knockdown of WDR5 significantly decreased SMC-marker gene expression in cultured SMC differentiation systems and in Xenopus laevis embryos in vivo. In addition, we showed that WDR5 complexes within SMC progenitor cells contained H3K4 methyltransferase enzymatic activity and that knockdown of WDR5 selectively decreased H3K4me1 and H3K4me3 enrichment within SMC-marker gene promoter loci. Moreover, we present evidence that it is recruited to these gene promoter loci through interaction with a SMC-selective pituitary homeobox 2 (Pitx2). Taken together, studies provide evidence for a novel mechanism for epigenetic control of SMC-marker gene expression during development through interaction of WDR5, homeodomain proteins, and chromatin remodeling enzymes.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role of WDR5 in silencing human fetal globin gene expression.Haematologica. 2012 Nov;97(11):1632-40. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2012.061937. Epub 2012 Jun 11. Haematologica. 2012. PMID: 22689669 Free PMC article.
-
WDR5 in porcine preimplantation embryos: expression, regulation of epigenetic modifications and requirement for early development†.Biol Reprod. 2017 Apr 1;96(4):758-771. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox020. Biol Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28379447
-
Pitx2 is functionally important in the early stages of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation.J Cell Biol. 2008 May 5;181(3):461-73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200711145. J Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18458156 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse roles of WDR5-RbBP5-ASH2L-DPY30 (WRAD) complex in the functions of the SET1 histone methyltransferase family.J Biosci. 2017 Mar;42(1):155-159. doi: 10.1007/s12038-017-9666-9. J Biosci. 2017. PMID: 28229975 Review.
-
The Development of Inhibitors Targeting the Mixed Lineage Leukemia 1 (MLL1)-WD Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5) Protein- Protein Interaction.Curr Med Chem. 2020;27(33):5530-5542. doi: 10.2174/0929867326666190528080514. Curr Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31132972 Review.
Cited by
-
The plasticity of WDR5 peptide-binding cleft enables the binding of the SET1 family of histone methyltransferases.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 May;40(9):4237-46. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1235. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22266653 Free PMC article.
-
PITX2 associates with PTIP-containing histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase complex.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Feb 21;444(4):634-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.143. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24486544 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 (nuclear paraspeckle assembly transcript 1) is critical for phenotypic switching of vascular smooth muscle cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 11;115(37):E8660-E8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803725115. Epub 2018 Aug 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30139920 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell function in atherosclerosis.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013 May;15(5):319. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013. PMID: 23630979 Review.
-
SMYD2 Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switching and Intimal Hyperplasia via Interaction with Myocardin.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 13:rs.3.rs-2721176. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2721176/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Aug 24;80(9):264. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04883-9. PMID: 37090651 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bernstein B. E., Mikkelsen T. S., Xie X., Kamal M., Huebert D. J., Cuff J., Fry B., Meissner A., Wernig M., Plath K., Jaenisch R., Wagschal A., Feil R., Schreiber S. L., Lander E. S. (2006) Cell 125, 315–326 - PubMed
-
- Mikkelsen T. S., Ku M., Jaffe D. B., Issac B., Lieberman E., Giannoukos G., Alvarez P., Brockman W., Kim T. K., Koche R. P., Lee W., Mendenhall E., O'Donovan A., Presser A., Russ C., Xie X., Meissner A., Wernig M., Jaenisch R., Nusbaum C., Lander E. S., Bernstein B. E. (2007) Nature 448, 553–560 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pan G., Tian S., Nie J., Yang C., Ruotti V., Wei H., Jonsdottir G. A., Stewart R., Thomson J. A. (2007) Cell Stem Cell 1, 299–312 - PubMed
-
- Zhao X. D., Han X., Chew J. L., Liu J., Chiu K. P., Choo A., Orlov Y. L., Sung W. K., Shahab A., Kuznetsov V. A., Bourque G., Oh S., Ruan Y., Ng H. H., Wei C. L. (2007) Cell Stem Cell 1, 286–298 - PubMed
-
- Lee J. H., Tate C. M., You J. S., Skalnik D. G. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 13419–13428 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

