Sprouty-related Ena/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein homology 1-domain-containing protein (SPRED1), a tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (SHP2) substrate in the Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway
- PMID: 21531714
- PMCID: PMC3123077
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.212662
Sprouty-related Ena/vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein homology 1-domain-containing protein (SPRED1), a tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 11 (SHP2) substrate in the Ras/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway
Abstract
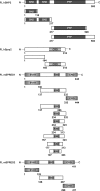
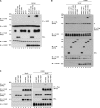
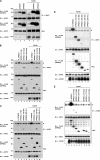
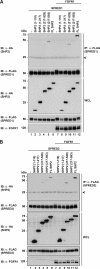
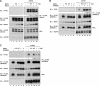
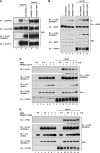
SHP2 is a tyrosine phosphatase involved in the activation of the Ras/ERK signaling pathway downstream of a number of receptor tyrosine kinases. One of the proposed mechanisms involving SHP2 in this context is to dephosphorylate and inactivate inhibitors of the Ras/ERK pathway. Two protein families bearing a unique, common domain, Sprouty and SPRED proteins, are possible candidates because they have been reported to inhibit the Ras/ERK pathway upon FGF activation. We tested whether any of these proteins are likely substrates of SHP2. Our findings indicate that Sprouty2 binds to the C-terminal tail of SHP2, which is an unlikely substrate binding site, whereas SPRED proteins bind to the tyrosine phosphatase domain that is known to be the binding site for its substrates. Overexpressed SHP2 was able to dephosphorylate SPREDs but not Sprouty2. Finally, we found two tyrosine residues on SPRED1 that are required, when phosphorylated, to inhibit Ras/ERK activation and identified Tyr-420 as a specific dephosphorylation target of SHP2. The evidence obtained indicates that SPRED1 is a likely substrate of SHP2, whose tyrosine dephosphorylation is required to attenuate the inhibitory action of SPRED1 in the Ras/ERK pathway.
Figures
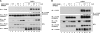
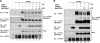
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

