EGFL6 promotes endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- PMID: 21531721
- PMCID: PMC3121348
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187633
EGFL6 promotes endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis through the activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase
Abstract
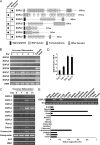
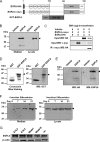
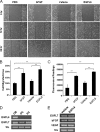
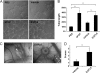
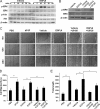
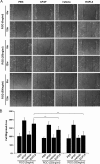
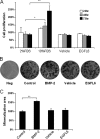
Angiogenesis is required for bone development, growth, and repair. It is influenced by the local bone environment that involves cross-talks between endothelial cells and adjacent bone cells. However, data regarding factors that directly contribute to angiogenesis by bone cells remain poorly understood. Here, we report that EGFL6, a member of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) repeat superfamily proteins, induces angiogenesis by a paracrine mechanism in which EGFL6 is expressed in osteoblastic-like cells but promotes migration and angiogenesis of endothelial cells. Co-immunoprecipitation assays revealed that EGFL6 is secreted in culture medium as a homodimer protein. Using scratch wound healing and transwell assays, we found that conditioned medium containing EGFL6 potentiates SVEC (a simian virus 40-transformed mouse microvascular endothelial cell line) endothelial cell migration. In addition, EGFL6 promotes the endothelial cell tube-like structure formation in Matrigel assays and angiogenesis in a chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane. Furthermore, we show that EGFL6 recombinant protein induces phosphorylation of ERK in SVEC endothelial cells. Inhibition of ERK impaired EGFL6-induced ERK activation and endothelial cell migration. Together, these results demonstrate, for the first time, that osteoblastic-like cells express EGFL6 that is capable of promoting endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis via ERK activation. Thus, the EGLF6 mediates a paracrine mechanism of cross-talk between vascular endothelial cells and osteoblasts and might offer an important new target for the potential treatment of bone diseases, including osteonecrosis, osteoporosis, and fracture healing.
Figures
References
-
- Brandi M. L., Collin-Osdoby P. (2006) J. Bone Miner. Res. 21, 183–192 - PubMed
-
- Gerber H. P., Ferrara N. (2000) Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 10, 223–228 - PubMed
-
- Carlevaro M. F., Cermelli S., Cancedda R., Descalzi Cancedda F. (2000) J. Cell Sci. 113, 59–69 - PubMed
-
- Hauge E. M., Qvesel D., Eriksen E. F., Mosekilde L., Melsen F. (2001) J. Bone Miner. Res. 16, 1575–1582 - PubMed
-
- Parfitt A. M. (2001) J. Bone Miner. Res. 16, 1583–1585 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

