Wnt signaling in the murine diastema
- PMID: 21531785
- PMCID: PMC3407839
- DOI: 10.1093/ejo/cjr049
Wnt signaling in the murine diastema
Abstract
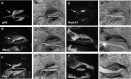
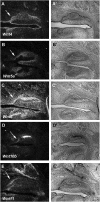
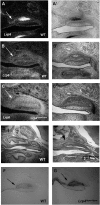
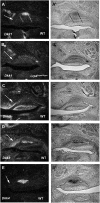
The correct number and shape of teeth are critical factors for an aesthetic and functional dentition. Understanding the molecular mechanisms regulating tooth number and shape are therefore important in orthodontics. Mice have only one incisor and three molars in each jaw quadrant that are divided by a tooth-less region, the diastema. Although mice lost teeth in the diastema during evolution, the remnants of the evolutionary lost teeth are observed as transient epithelial buds in the wild-type diastema during early stages of development. Shh and Fgf signaling pathways that are essential for tooth development have been shown to be repressed in the diastema. It remains unclear however how Wnt signaling, that is also required for tooth development, is regulated in the diastema. In this study we found that in the embryonic diastema, Wnt5a expression was observed in mesenchyme, whereas Wnt4 and Wnt10b were expressed in epithelium. The expression of Wnt6 and Wnt11 was found in both tissues. The Wnt co-receptor, Lrp6, was weakly expressed in the diastema overlapping with weak Lrp4 expression, a co-receptor that inhibits Wnt signaling. Secreted Wnt inihibitors Dkk1, Dkk2, and Dkk3 were also expressed in the diastema. Lrp4 mutant mice develop supernumerary teeth in the diastema that is accompanied by upregulation of Wnt signaling and Lrp6 expression. Wnt signaling is thus usually attenuated in the diastema by these secreted and membrane bound Wnt inhibitors.
Figures
References
-
- Andl T, Reddy ST, Gaddapara T, Millar SE. Wnt signals are required for the initiation of hair follicle development. Developmental Cell. 2002;2:643–653. - PubMed
-
- Bafico A, Liu G, Yaniv A, Gazit A, Aaronson SA. Novel mechanism of wnt signalling inhibition mediated by dickkopf-1 interaction with lrp6/arrow. Nature Cell Biology. 2001;3:683–686. - PubMed
-
- Butler PM. Studies of the mammalian dentition-differentiation of the post-canine dentition. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 1939;B109:1–36.
-
- Clevers H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell. 2006;127:469–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

