Differential pathways regulating innate and adaptive antitumor immune responses by particulate and soluble yeast-derived β-glucans
- PMID: 21531981
- PMCID: PMC3128477
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-339812
Differential pathways regulating innate and adaptive antitumor immune responses by particulate and soluble yeast-derived β-glucans
Abstract
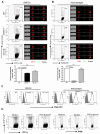
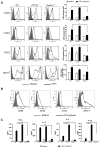
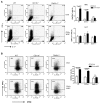
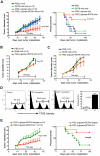
β-glucans have been reported to function as a potent adjuvant to stimulate innate and adaptive immune responses. However, β-glucans from different sources are differential in their structure, conformation, and thus biologic activity. Different preparations of β-glucans, soluble versus particulate, further complicate their mechanism of action. Here we show that yeast-derived particulate β-glucan activated dendritic cells (DCs) and macrophages via a C-type lectin receptor dectin-1 pathway. Activated DCs by particulate β-glucan promoted Th1 and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte priming and differentiation in vitro. Treatment of orally administered yeast-derived particulate β-glucan elicited potent antitumor immune responses and drastically down-regulated immunosuppressive cells, leading to the delayed tumor progression. Deficiency of the dectin-1 receptor completely abrogated particulate β-glucan-mediated antitumor effects. In contrast, yeast-derived soluble β-glucan bound to DCs and macrophages independent of the dectin-1 receptor and did not activate DCs. Soluble β-glucan alone had no therapeutic effect but significantly augmented antitumor monoclonal antibody-mediated therapeutic efficacy via a complement activation pathway but independent of dectin-1 receptor. These findings reveal the importance of different preparations of β-glucans in the adjuvant therapy and allow for the rational design of immunotherapeutic protocols usable in clinical trials.
Figures


References
-
- Smyth MJ, Hayakawa Y, Cretney E, et al. IL-21 enhances tumor-specific CTL induction by anti-DR5 antibody therapy. J Immunol. 2006;176(10):6347–6355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

