Nanodisc-based co-immunoprecipitation for mass spectrometric identification of membrane-interacting proteins
- PMID: 21532009
- PMCID: PMC3134077
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.O110.006775
Nanodisc-based co-immunoprecipitation for mass spectrometric identification of membrane-interacting proteins
Abstract
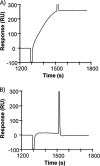
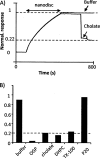
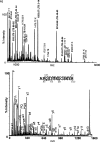
Proteomic identification of protein interactions with membrane associated molecules in their native membrane environment pose a challenge because of technical problems of membrane handling. We investigate the possibility of employing membrane nanodiscs for harboring the membrane associated molecule to tackle the challenges. Nanodiscs are stable, homogenous pieces of membrane with a discoidal shape. They are stabilized by an encircling amphipatic protein with an engineered epitope tag. In the present study we employ the epitope tag of the nanodiscs for detection and co-immunoprecipitation of interaction partners of the glycolipid ganglioside GM1 harbored by nanodiscs. Highly specific binding activity for nanodisc-GM1 immobilized on sensorchips was observed by surface plasmon resonance in culture media from enterotoxigenic Escherischia coli. To isolate the interaction partner(s) from enterotoxigenic Escherischia coli, GM1-nanodiscs were employed for co-immunoprecipitation. The B subunit of heat labile enterotoxin was identified as a specific interaction partner by mass spectrometry, thus demonstrating that nanodisc technology is useful for highly specific detection and identification of interaction partners to specific lipids embedded in a membrane bilayer.
Figures

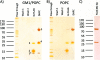
Similar articles
-
Nanodiscs for immobilization of lipid bilayers and membrane receptors: kinetic analysis of cholera toxin binding to a glycolipid receptor.Anal Chem. 2008 Aug 15;80(16):6245-52. doi: 10.1021/ac8000644. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Anal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18616345
-
Label-free detection and identification of protein ligands captured by receptors in a polymerized planar lipid bilayer using MALDI-TOF MS.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015 Apr;407(10):2777-89. doi: 10.1007/s00216-015-8508-6. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015. PMID: 25694144 Free PMC article.
-
High-Affinity Binding of Monomeric but Not Oligomeric Amyloid-β to Ganglioside GM1 Containing Nanodiscs.Biochemistry. 2016 Dec 6;55(48):6662-6672. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00829. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27933798
-
The nanodisc: a novel tool for membrane protein studies.Biol Chem. 2009 Aug;390(8):805-14. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.091. Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19453280 Review.
-
Phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs: a powerful tool to study the structural organization and biochemical reactivity of proteins in membrane-like environments.Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14(23):2637-46. doi: 10.2174/1568026614666141215142951. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25515754 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanodisc-solubilized membrane protein library reflects the membrane proteome.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013 May;405(12):4009-16. doi: 10.1007/s00216-013-6790-8. Epub 2013 Feb 12. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2013. PMID: 23400332 Free PMC article.
-
Ice breaking in GPCR structural biology.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Mar;33(3):324-34. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.187. Epub 2012 Jan 30. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22286917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in membrane mimetics for membrane protein research.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Jun 28;51(3):1405-1416. doi: 10.1042/BST20230164. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37345653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultra-thin layer MALDI mass spectrometry of membrane proteins in nanodiscs.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012 Jan;402(2):721-9. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5512-3. Epub 2011 Nov 6. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22057720 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodiscs in Membrane Biochemistry and Biophysics.Chem Rev. 2017 Mar 22;117(6):4669-4713. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00690. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Chem Rev. 2017. PMID: 28177242 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hunte C., von Jagow G., Schägger H. (2003) Membrane protein purification and crystallization a practical guide. Academic Press, Oxford
-
- Torchilin V. P., Weissig V. (2003) Liposomes, A practical approach, second ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford
-
- Selinsky B. S. (2003) Membrane protein protocols. Expression, purification, and characterization, Methods in Molecular Biology, Humana Press, Hohokus, NJ
-
- Borch J., Hamann T. (2009) The nanodisc: a novel tool for membrane protein studies. Biol. Chem. 390, 805–814 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

