Anti-inflammatory therapeutics for the treatment of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 21532566
- PMCID: PMC3947588
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd3444
Anti-inflammatory therapeutics for the treatment of atherosclerosis
Abstract
Atherosclerosis is the primary cause of heart disease and stroke and is thus the underlying pathology of the leading causes of death in the western world. Although risk can be reduced by lowering lipid levels, the equally important contribution of inflammation to the development of cardiovascular disease is not adequately addressed by existing therapies. Here, we summarize the evidence supporting a role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, discuss agents that are currently in the clinic and provide a perspective on the challenges faced in the development of drugs that target vascular inflammation.
Figures
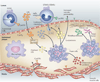

References
-
- National Institutes of Health: National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. 2009 NHLBI Morbidity and Mortality Chart Book. National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. 2009 [online], http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/resources/docs/2009_ChartBook.pdf.
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis — an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;340:115–126. - PubMed
-
- Glass CK, Witztum JL. Atherosclerosis: the road ahead. Cell. 2001;104:503–516. - PubMed
-
- Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–874. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

