Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity
- PMID: 21532591
- PMCID: PMC3102791
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09968
Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity
Abstract
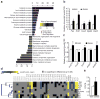
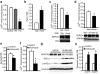
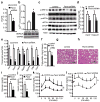
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the main site of protein and lipid synthesis, membrane biogenesis, xenobiotic detoxification and cellular calcium storage, and perturbation of ER homeostasis leads to stress and the activation of the unfolded protein response. Chronic activation of ER stress has been shown to have an important role in the development of insulin resistance and diabetes in obesity. However, the mechanisms that lead to chronic ER stress in a metabolic context in general, and in obesity in particular, are not understood. Here we comparatively examined the proteomic and lipidomic landscape of hepatic ER purified from lean and obese mice to explore the mechanisms of chronic ER stress in obesity. We found suppression of protein but stimulation of lipid synthesis in the obese ER without significant alterations in chaperone content. Alterations in ER fatty acid and lipid composition result in the inhibition of sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) activity and ER stress. Correcting the obesity-induced alteration of ER phospholipid composition or hepatic Serca overexpression in vivo both reduced chronic ER stress and improved glucose homeostasis. Hence, we established that abnormal lipid and calcium metabolism are important contributors to hepatic ER stress in obesity.
Figures

Comment in
-
Obesity: a step forward in understanding endoplasmic reticulum stress.Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011 Jul 4;8(7):360. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.93. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21725345 No abstract available.
-
Hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity: deeper insights into processes, but are they relevant to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis?Hepatology. 2011 Dec;54(6):2260-5. doi: 10.1002/hep.24661. Hepatology. 2011. PMID: 22139704 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(7):519. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, et al. Enrichment of endoplasmic reticulum with cholesterol inhibits sarcoplasmic-endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase-2b activity in parallel with increased order of membrane lipids: implications for depletion of endoplasmic reticulum calcium stores and apoptosis in cholesterol-loaded macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(35):37030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

