p38γ mitogen-activated protein kinase contributes to oncogenic properties maintenance and resistance to poly (ADP-ribose)-polymerase-1 inhibition in breast cancer
- PMID: 21532888
- PMCID: PMC3084624
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.101748
p38γ mitogen-activated protein kinase contributes to oncogenic properties maintenance and resistance to poly (ADP-ribose)-polymerase-1 inhibition in breast cancer
Abstract
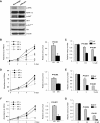
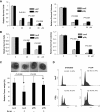
p38γ MAPK, one of the four members of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), has previously been shown to harbor oncogenic functions. However, the biologic function of p38γ MAPK in breast cancer has not been well defined. In this study, we have shown that p38γ MAPK is overexpressed in highly metastatic human and mouse breast cancer cell lines and p38γ MAPK expression is preferentially associated with basal-like and metastatic phenotypes of breast tumor samples. Ectopic expression of p38γ MAPK did not lead to an increase in oncogenic properties in vitro in most tested mammary epithelial cells. However, knockdown of p38γ MAPK expression resulted in a dramatic decrease in cell proliferation, colony formation, cell migration, invasion in vitro and significant retardation of tumorigenesis, and long-distance metastasis to the lungs in vivo. Moreover, knockdown of p38γ MAPK triggered the activation of AKT signaling. Inhibition of this feedback loop with various PI3K/AKT signaling inhibitors facilitated the effect of targeting p38γ MAPK. We further found that overexpression of p38γ MAPK did not promote cell resistance to chemotherapeutic agents doxorubicin and paclitaxel but significantly increased cell resistance to PJ-34, a DNA damage agent poly (ADP-ribose)-polymerase-1 (PARP) inhibitor in vitro and in vivo. Finally, we identified that p38γ MAPK overexpression led to marked cell cycle arrest in G(2)/M phase. Our study for the first time clearly demonstrates that p38γ MAPK is a promising target for the design of targeted therapies for basal-like breast cancer with metastatic characteristics and for overcoming potential resistance against the PARP inhibitor.
Figures





References
-
- Cuenda A, Rousseau S. p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1358–1375. - PubMed
-
- Dhanasekaran DN, Johnson GL. MAPKs: function, regulation, role in cancer and therapeutic targeting. Oncogene. 2007;26:3097–3099. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Lee JD, Bibbs L, Ulevitch RJ. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994;265:808–811. - PubMed
-
- Jiang Y, Chen C, Li Z, Guo W, Gegner JA, Lin S, Han J. Characterization of the structure and function of a new mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38β) J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17920–17926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
