Loss of ATF2 function leads to cranial motoneuron degeneration during embryonic mouse development
- PMID: 21533046
- PMCID: PMC3080913
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019090
Loss of ATF2 function leads to cranial motoneuron degeneration during embryonic mouse development
Abstract
The AP-1 family transcription factor ATF2 is essential for development and tissue maintenance in mammals. In particular, ATF2 is highly expressed and activated in the brain and previous studies using mouse knockouts have confirmed its requirement in the cerebellum as well as in vestibular sense organs. Here we present the analysis of the requirement for ATF2 in CNS development in mouse embryos, specifically in the brainstem. We discovered that neuron-specific inactivation of ATF2 leads to significant loss of motoneurons of the hypoglossal, abducens and facial nuclei. While the generation of ATF2 mutant motoneurons appears normal during early development, they undergo caspase-dependent and independent cell death during later embryonic and foetal stages. The loss of these motoneurons correlates with increased levels of stress activated MAP kinases, JNK and p38, as well as aberrant accumulation of phosphorylated neurofilament proteins, NF-H and NF-M, known substrates for these kinases. This, together with other neuropathological phenotypes, including aberrant vacuolisation and lipid accumulation, indicates that deficiency in ATF2 leads to neurodegeneration of subsets of somatic and visceral motoneurons of the brainstem. It also confirms that ATF2 has a critical role in limiting the activities of stress kinases JNK and p38 which are potent inducers of cell death in the CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
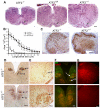
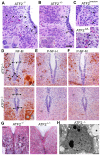

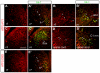
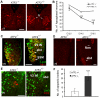




References
-
- Herdegen T, Leah JD. Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998;28:370–490. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Campbell D, Derijard B, Davis RJ. Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science. 1995;267:389–393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

