Lysophosphatidic acid activates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ in CHO cells that over-express glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase-1
- PMID: 21533082
- PMCID: PMC3080373
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018932
Lysophosphatidic acid activates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ in CHO cells that over-express glycerol 3-phosphate acyltransferase-1
Abstract
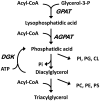
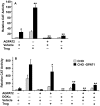
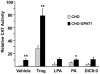
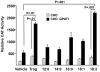
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is an agonist for peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ (PPARγ). Although glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-1 (GPAT1) esterifies glycerol-3-phosphate to form LPA, an intermediate in the de novo synthesis of glycerolipids, it has been assumed that LPA synthesized by this route does not have a signaling role. The availability of Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells that stably overexpress GPAT1, allowed us to analyze PPARγ activation in the presence of LPA produced as an intracellular intermediate. LPA levels in CHO-GPAT1 cells were 6-fold higher than in wild-type CHO cells, and the mRNA abundance of CD36, a PPARγ target, was 2-fold higher. Transactivation assays showed that PPARγ activity was higher in the cells that overexpressed GPAT1. PPARγ activity was enhanced further in CHO-GPAT1 cells treated with the PPARγ ligand troglitazone. Extracellular LPA, phosphatidic acid (PA) or a membrane-permeable diacylglycerol had no effect, showing that PPARγ had been activated by LPA generated intracellularly. Transient transfection of a vector expressing 1-acylglycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-2, which converts endogenous LPA to PA, markedly reduced PPARγ activity, as did over-expressing diacylglycerol kinase, which converts DAG to PA, indicating that PA could be a potent inhibitor of PPARγ. These data suggest that LPA synthesized via the glycerol-3-phosphate pathway can activate PPARγ and that intermediates of de novo glycerolipid synthesis regulate gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Gervois P, Fruchart J-C, Staels B. Inflammation, dyslipidaemia, diabetes and PPARs: pharmacological interest of dual PPARa and PPARg agonists. Int J Clin Pract. 2004;58:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Berger J, Moller DE. The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:409–435. - PubMed
-
- Moolenaar WH, van Meeteren LA, Giepmans BN. The ins and outs of lysophosphatidic acid signaling. Bioessays. 2004;26:870–881. - PubMed
-
- Tsukahara T, Tsukahara R, Yasuda S, Makarova N, Valentine WJ, et al. Different residues mediate recognition of 1-O-oleyl-lysophosphatidic acid and rosiglitazone in the ligand binding domain of PPARg. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:3398–3407. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK59935/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK68993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK068993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059935/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK59635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK056598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK40936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK56598/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK34987/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

