Arabidopsis plasmodesmal proteome
- PMID: 21533090
- PMCID: PMC3080382
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018880
Arabidopsis plasmodesmal proteome
Abstract
The multicellular nature of plants requires that cells should communicate in order to coordinate essential functions. This is achieved in part by molecular flux through pores in the cell wall, called plasmodesmata. We describe the proteomic analysis of plasmodesmata purified from the walls of Arabidopsis suspension cells. Isolated plasmodesmata were seen as membrane-rich structures largely devoid of immunoreactive markers for the plasma membrane, endoplasmic reticulum and cytoplasmic components. Using nano-liquid chromatography and an Orbitrap ion-trap tandem mass spectrometer, 1341 proteins were identified. We refer to this list as the plasmodesmata- or PD-proteome. Relative to other cell wall proteomes, the PD-proteome is depleted in wall proteins and enriched for membrane proteins, but still has a significant number (35%) of putative cytoplasmic contaminants, probably reflecting the sensitivity of the proteomic detection system. To validate the PD-proteome we searched for known plasmodesmal proteins and used molecular and cell biological techniques to identify novel putative plasmodesmal proteins from a small subset of candidates. The PD-proteome contained known plasmodesmal proteins and some inferred plasmodesmal proteins, based upon sequence or functional homology with examples identified in different plant systems. Many of these had a membrane association reflecting the membranous nature of isolated structures. Exploiting this connection we analysed a sample of the abundant receptor-like class of membrane proteins and a small random selection of other membrane proteins for their ability to target plasmodesmata as fluorescently-tagged fusion proteins. From 15 candidates we identified three receptor-like kinases, a tetraspanin and a protein of unknown function as novel potential plasmodesmal proteins. Together with published work, these data suggest that the membranous elements in plasmodesmata may be rich in receptor-like functions, and they validate the content of the PD-proteome as a valuable resource for the further uncovering of the structure and function of plasmodesmata as key components in cell-to-cell communication in plants.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
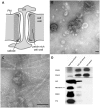

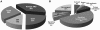
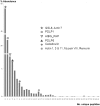
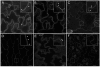
References
-
- Lucas WJ, Ham LK, Kim JY. Plasmodesmata - bridging the gap between neighboring plant cells. Trends Cell Biol. 2009;19:495–503. - PubMed
-
- Oparka KJ. Getting the message across: how do plant cells exchange macromolecular complexes? Trends Plant Sci. 2004;9:33–41. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner C, Maule A. Opportunities and successes in the search for plasmodesmal proteins. Protoplasma. 2011;248:27–38. - PubMed
-
- Overall RL, Blackman LM. A model of the macromolecular structure of plasmodesmata. Trends Plant Sci. 1996;1:307–311.
-
- Botha CE, Cross RH. Towards reconciliation of structure with function in plasmodesmata-who is the gatekeeper? Micron. 2000;31:713–721. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

