Functional connectivity fMRI of the rodent brain: comparison of functional connectivity networks in rat and mouse
- PMID: 21533116
- PMCID: PMC3078931
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018876
Functional connectivity fMRI of the rodent brain: comparison of functional connectivity networks in rat and mouse
Abstract
At present, resting state functional MRI (rsfMRI) is increasingly used in human neuropathological research. The present study aims at implementing rsfMRI in mice, a species that holds the widest variety of neurological disease models. Moreover, by acquiring rsfMRI data with a comparable protocol for anesthesia, scanning and analysis, in both rats and mice we were able to compare findings obtained in both species. The outcome of rsfMRI is different for rats and mice and depends strongly on the applied number of components in the Independent Component Analysis (ICA). The most important difference was the appearance of unilateral cortical components for the mouse resting state data compared to bilateral rat cortical networks. Furthermore, a higher number of components was needed for the ICA analysis to separate different cortical regions in mice as compared to rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
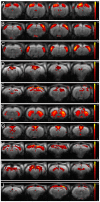
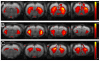




References
-
- Biswal B, Yetkin FZ, Haughton VM, Hyde JS. Functional connectivity in the motor cortex of resting human brain using echo-planar MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1995;34:537–541. - PubMed
-
- van den Heuvel MP, Hulshoff Pol HE. Exploring the brain network: a review on resting-state fMRI functional connectivity. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010;20:519–534. - PubMed
-
- Damoiseaux JS, Beckmann CF, Arigita EJ, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, et al. Reduced resting-state brain activity in the “default network” in normal aging. Cereb Cortex. 2008;18:1856–1864. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

