The anti-apoptotic Bcl-x(L) protein, a new piece in the puzzle of cytochrome c interactome
- PMID: 21533126
- PMCID: PMC3080137
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018329
The anti-apoptotic Bcl-x(L) protein, a new piece in the puzzle of cytochrome c interactome
Abstract
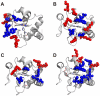
A structural model of the adduct between human cytochrome c and the human anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-x(L), which defines the protein-protein interaction surface, was obtained from solution NMR chemical shift perturbation data. The atomic level information reveals key intermolecular contacts identifying new potentially druggable areas on cytochrome c and Bcl-x(L). Involvement of residues on cytochrome c other than those in its complexes with electron transfer partners is apparent. Key differences in the contact area also exist between the Bcl-x(L) adduct with the Bak peptide and that with cytochrome c. The present model provides insights to the mechanism by which cytochrome c translocated to cytosol can be intercepted, so that the apoptosome is not assembled.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Scott RA, Mauk AG. Cytochrome c. A multidisciplinary approach. Sausalito, California: University Science Books; 1996.
-
- Bertini I, Cavallaro G, Rosato A. Cytochrome c: occurrence and functions. Chem Rev. 2006;106:90–115. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X. Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell (Cambridge,Mass) 1996;86:147–157. - PubMed
-
- Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, et al. Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell (Cambridge,Mass) 1997;91:479–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

