The PLIN4 variant rs8887 modulates obesity related phenotypes in humans through creation of a novel miR-522 seed site
- PMID: 21533135
- PMCID: PMC3080366
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017944
The PLIN4 variant rs8887 modulates obesity related phenotypes in humans through creation of a novel miR-522 seed site
Abstract
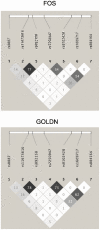
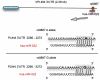
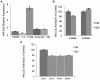
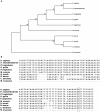
PLIN4 is a member of the PAT family of lipid storage droplet (LSD) proteins. Associations between seven single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) at human PLIN4 with obesity related phenotypes were investigated using meta-analysis followed by a determination if these phenotypes are modulated by interactions between PLIN4 SNPs and dietary PUFA. Samples consisted of subjects from two populations of European ancestry. We demonstrated association of rs8887 with anthropometrics. Meta-analysis demonstrated significant interactions between the rs8887 minor allele with PUFA n3 modulating anthropometrics. rs884164 showed interaction with both n3 and n6 PUFA modulating anthropometric and lipid phenotypes. In silico analysis of the PLIN4 3'UTR sequence surrounding the rs8887 minor A allele predicted a seed site for the human microRNA-522 (miR-522), suggesting a functional mechanism. Our data showed that a PLIN4 3'UTR luciferase reporter carrying the A allele of rs8887 was reduced in response to miR-522 mimics compared to the G allele. These results suggest variation at the PLIN4 locus, and its interaction with PUFA as a modulator of obesity related phenotypes, acts in part through creation of a miR-522 regulatory site.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ogden C. Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association. 2006;295:1549–1555. - PubMed
-
- Fontaine KR, Redden DT, Wang C, Westfall AO, Allison DB. Years of life lost due to obesity. JAMA. 2003;289:187–193. - PubMed
-
- Koutsari C. Thematic review series: Patient-Oriented Research. Free fatty acid metabolism in human obesity. The Journal of Lipid Research. 2006;47:1643–1650. - PubMed
-
- Vanherpen N, Schrauwenhinderling V. Lipid accumulation in non-adipose tissue and lipotoxicity. Physiol Behav. 2008;94:231–241. - PubMed
-
- Brasaemle DL. Thematic review series: Adipocyte Biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J Lipid Res. 2007;48:2547–2559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

