Gastrectomy alters emotional reactivity in rats: neurobiological mechanisms
- PMID: 21535247
- PMCID: PMC3110309
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07640.x
Gastrectomy alters emotional reactivity in rats: neurobiological mechanisms
Abstract
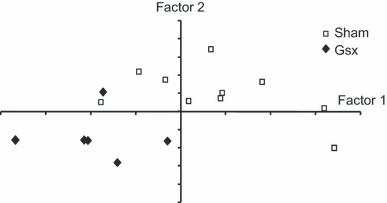
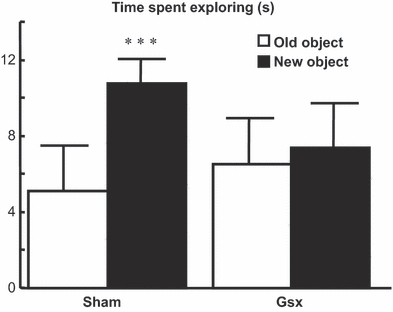
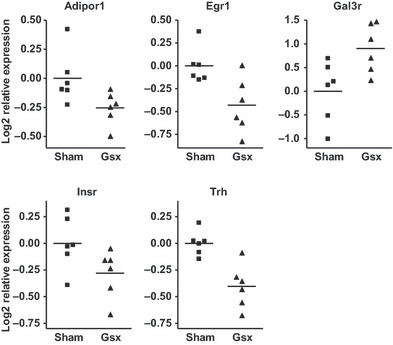
Gastrectomy (Gsx) is associated with altered emotional function and a predisposition to depression/anxiety disorders. Here we investigated the effects of Gsx on emotional reactivity in rats and explored the underlying neurobiological mechanisms. Gsx- and sham-operated rats were exposed to behavioural tests that explore anxiety- and depression-like behaviour (open field, black and white box, elevated plus maze, social interaction, forced swim) as well as memory (object recognition). The potential neurobiological mechanisms underlying these differences were explored by measuring (i) turnover of candidate neurotransmitter systems in the nucleus accumbens, (ii) hippocampal neurogenesis by BrdU labelling or by analysis of candidate genes involved in neuronal growth and (iii) changes in mRNA expression of candidate genes in dissected hippocampal and amygdala tissue. Data from individual behavioural tests as well as from multivariate analysis revealed differing emotional reactivity between Gsx- and sham-operated rats. Gsx rats showed reduced emotional reactivity in a new environment and decreased depression-like behaviour. Accumbal serotonin and dopamine turnover were both reduced in Gsx rats. Gsx also led to a memory deficit, although hippocampal neurogenesis was unaffected. Of the many candidate genes studied by real-time RT-PCR, we highlight a Gsx-associated decrease in expression of Egr-1, a transcription factor linked to neural plasticity and cognition, in the hippocampus and amygdala. Thus, Gsx induces an alteration of emotional reactivity and a memory/cognitive deficit that is associated with reduced turnover of serotonin and dopamine in the nucleus accumbens and decreased expression of Egr-1 in the hippocampus and amygdala.
© 2011 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2011 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The amygdala and emotional modulation of competition between cognitive and habit memory.Behav Brain Res. 2008 Nov 3;193(1):126-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2008.05.002. Epub 2008 May 8. Behav Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18565602
-
Chronic REM Sleep Restriction in Juvenile Male Rats Induces Anxiety-Like Behavior and Alters Monoamine Systems in the Amygdala and Hippocampus.Mol Neurobiol. 2018 Apr;55(4):2884-2896. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0541-3. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 28455701
-
Serotonin laterality in amygdala predicts performance in the elevated plus maze in rats.Neuroreport. 1999 Nov 26;10(17):3497-500. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199911260-00006. Neuroreport. 1999. PMID: 10619632
-
Adaptive emotional memory: the key hippocampal-amygdalar interaction.Stress. 2015;18(3):297-308. doi: 10.3109/10253890.2015.1067676. Epub 2015 Aug 11. Stress. 2015. PMID: 26260664 Review.
-
Neurobehavioural sequelae of social deprivation in rodents revisited: Modelling social adversity for developmental neuropsychiatric disorders.J Psychopharmacol. 2016 Nov;30(11):1082-1089. doi: 10.1177/0269881116664450. Epub 2016 Sep 26. J Psychopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27678088 Review.
Cited by
-
What influences food choices in anorexia nervosa? Disentangling cognitive and emotional components of decision-making by translational research.Neurosci Appl. 2024 Jun 22;3:104080. doi: 10.1016/j.nsa.2024.104080. eCollection 2024. Neurosci Appl. 2024. PMID: 40656109 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguilar-Valles A, Sanchez E, de Gortari P, Garcia-Vazquez AI, Ramirez-Amaya V, Bermudez-Rattoni F, Joseph-Bravo P. The expression of TRH, its receptors and degrading enzyme is differentially modulated in the rat limbic system during training in the Morris water maze. Neurochem. Int. 2007;50:404–417. - PubMed
-
- Ariyasu H, Takaya K, Tagami T, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Akamizu T, Suda M, Koh T, Natsui K, Toyooka S, Shirakami G, Usui T, Shimatsu A, Doi K, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K. Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;86:4753–4758. - PubMed
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Kaga T, Yuzuriha H, Nagata T, Fujimiya M, Katsuura G, Makino S, Fujino MA, Kasuga M. A role of ghrelin in neuroendocrine and behavioral responses to stress in mice. Neuroendocrinology. 2001;74:143–147. - PubMed
-
- Barazzoni R, Zanetti M, Stulle M, Mucci MP, Pirulli A, Dore F, Panzetta G, Vasile A, Biolo G, Guarnieri G. Higher total ghrelin levels are associated with higher insulin-mediated glucose disposal in non-diabetic maintenance hemodialysis patients. Clin. Nutr. 2008;27:142–149. - PubMed
-
- Bjartmar L, Johansson IM, Marcusson J, Ross SB, Seckl JR, Olsson T. Selective effects on NGFI-A, MR, GR and NGFI-B hippocampal mRNA expression after chronic treatment with different subclasses of antidepressants in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2000;151:7–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

