A deficiency of uPAR alters endothelial angiogenic function and cell morphology
- PMID: 21535874
- PMCID: PMC3105951
- DOI: 10.1186/2045-824X-3-10
A deficiency of uPAR alters endothelial angiogenic function and cell morphology
Abstract
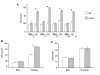
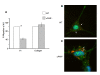
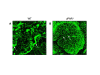
The angiogenic potential of a cell requires dynamic reorganization of the cytoskeletal architecture that involves the interaction of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) with the extracellular matrix. This study focuses on the effect of uPAR deficiency (uPAR-/-) on angiogenic function and associated cytoskeletal organization. Utilizing murine endothelial cells, it was observed that adhesion, migration, proliferation, and capillary tube formation were altered in uPAR-/- cells compared to wild-type (WT) cells. On a vitronectin (Vn) matrix, uPAR-/- cells acquired a "fried egg" morphology characterized by circular actin organization and lack of lamellipodia formation. The up-regulation of β1 integrin, FAK(P-Tyr925), and paxillin (P-Tyr118), and decreased Rac1 activation, suggested increased focal adhesions, but delayed focal adhesion turnover in uPAR-/- cells. This accounted for the enhanced adhesion, but attenuated migration, on Vn. VEGF-enriched Matrigel implants from uPAR-/- mice demonstrated a lack of mature vessel formation compared to WT mice. Collectively, these results indicate that a uPAR deficiency leads to decreased angiogenic functions of endothelial cells.
Figures







References
-
- Ingber DE. Mechanical signaling and the cellular response to extracellular matrix in angiogenesis and cardiovascular physiology. Circ Res. 2002;15:877–887. - PubMed
-
- Rabbani SA, Mazar AP. The role of the plasminogen activation system in angiogenesis and metastasis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2001;10:393–415. - PubMed
-
- Stoppelli MP, Corti A, Soffientini A, Cassani G, Blasi F, Assoian RK. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1985;82:4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

