De novo assembly and validation of planaria transcriptome by massive parallel sequencing and shotgun proteomics
- PMID: 21536722
- PMCID: PMC3129261
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.113779.110
De novo assembly and validation of planaria transcriptome by massive parallel sequencing and shotgun proteomics
Abstract
Freshwater planaria are a very attractive model system for stem cell biology, tissue homeostasis, and regeneration. The genome of the planarian Schmidtea mediterranea has recently been sequenced and is estimated to contain >20,000 protein-encoding genes. However, the characterization of its transcriptome is far from complete. Furthermore, not a single proteome of the entire phylum has been assayed on a genome-wide level. We devised an efficient sequencing strategy that allowed us to de novo assemble a major fraction of the S. mediterranea transcriptome. We then used independent assays and massive shotgun proteomics to validate the authenticity of transcripts. In total, our de novo assembly yielded 18,619 candidate transcripts with a mean length of 1118 nt after filtering. A total of 17,564 candidate transcripts could be mapped to 15,284 distinct loci on the current genome reference sequence. RACE confirmed complete or almost complete 5' and 3' ends for 22/24 transcripts. The frequencies of frame shifts, fusion, and fission events in the assembled transcripts were computationally estimated to be 4.2%-13%, 0%-3.7%, and 2.6%, respectively. Our shotgun proteomics produced 16,135 distinct peptides that validated 4200 transcripts (FDR ≤1%). The catalog of transcripts assembled in this study, together with the identified peptides, dramatically expands and refines planarian gene annotation, demonstrated by validation of several previously unknown transcripts with stem cell-dependent expression patterns. In addition, our robust transcriptome characterization pipeline could be applied to other organisms without genome assembly. All of our data, including homology annotation, are freely available at SmedGD, the S. mediterranea genome database.
Figures
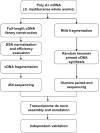
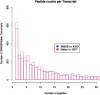
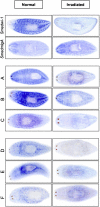
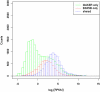
References
-
- Agata K 2003. Regeneration and gene regulation in planarians. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13: 492–496 - PubMed
-
- Alexeyenko A, Tamas I, Liu G, Sonnhammer ELL 2006. Automatic clustering of orthologs and inparalogs shared by multiple proteomes. Bioinformatics 22: e9–e15 - PubMed
-
- Cox J, Mann M 2008. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat Biotechnol 26: 1367–1372 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
