Uncoupling of GTP hydrolysis from eIF6 release on the ribosome causes Shwachman-Diamond syndrome
- PMID: 21536732
- PMCID: PMC3084026
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.623011
Uncoupling of GTP hydrolysis from eIF6 release on the ribosome causes Shwachman-Diamond syndrome
Abstract
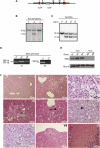
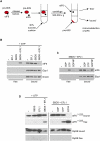
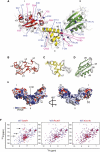
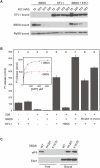
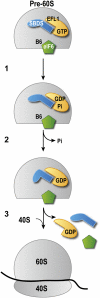
Removal of the assembly factor eukaryotic initiation factor 6 (eIF6) is critical for late cytoplasmic maturation of 60S ribosomal subunits. In mammalian cells, the current model posits that eIF6 release is triggered following phosphorylation of Ser 235 by activated protein kinase C. In contrast, genetic studies in yeast indicate a requirement for the ortholog of the SBDS (Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome) gene that is mutated in the inherited leukemia predisposition disorder Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS). Here, by isolating late cytoplasmic 60S ribosomal subunits from Sbds-deleted mice, we show that SBDS and the GTPase elongation factor-like 1 (EFL1) directly catalyze eIF6 removal in mammalian cells by a mechanism that requires GTP binding and hydrolysis by EFL1 but not phosphorylation of eIF6 Ser 235. Functional analysis of disease-associated missense variants reveals that the essential role of SBDS is to tightly couple GTP hydrolysis by EFL1 on the ribosome to eIF6 release. Furthermore, complementary NMR spectroscopic studies suggest unanticipated mechanistic parallels between this late step in 60S maturation and aspects of bacterial ribosome disassembly. Our findings establish a direct role for SBDS and EFL1 in catalyzing the translational activation of ribosomes in all eukaryotes, and define SDS as a ribosomopathy caused by uncoupling GTP hydrolysis from eIF6 release.
Figures


Comment in
-
Of blood, bones, and ribosomes: is Swachman-Diamond syndrome a ribosomopathy?Genes Dev. 2011 May 1;25(9):898-900. doi: 10.1101/gad.2053011. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21536731 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barlow JL, Drynan LF, Trim NL, Erber WN, Warren AJ, McKenzie AN 2010b. New insights into 5q− syndrome as a ribosomopathy. Cell Cycle 9: 4286–4293 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
