Phosphoinositide [PI(3,5)P2] lipid-dependent regulation of the general transcriptional regulator Tup1
- PMID: 21536737
- PMCID: PMC3084031
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1998611
Phosphoinositide [PI(3,5)P2] lipid-dependent regulation of the general transcriptional regulator Tup1
Abstract
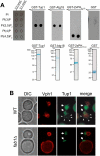
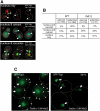
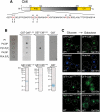
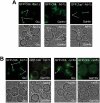
Transcriptional activity of a gene is governed by transcriptional regulatory complexes that assemble/disassemble on the gene and control the chromatin architecture. How cytoplasmic components influence the assembly/disassembly of transcriptional regulatory complexes is poorly understood. Here we report that the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has a chromatin architecture-modulating mechanism that is dependent on the endosomal lipid PI(3,5)P(2). We identified Tup1 and Cti6 as new, highly specific PI(3,5)P(2) interactors. Tup1--which associates with multiple transcriptional regulators, including the HDAC (histone deacetylase) and SAGA complexes--plays a crucial role in determining an activated or repressed chromatin state of numerous genes, including GAL1. We show that, in the context that the Gal4 activation pathway is compromised, PI(3,5)P(2) plays an essential role in converting the Tup1-driven repressed chromatin structure into a SAGA-containing activated chromatin structure at the GAL1 promoter. Biochemical and cell biological experiments suggest that PI(3,5)P(2) recruits Cti6 and the Cyc8-Tup1 corepressor complex to the late endosomal/vacuolar membrane and mediates the assembly of a Cti6-Cyc8-Tup1 coactivator complex that functions to recruit the SAGA complex to the GAL1 promoter. Our findings provide important insights toward understanding how the chromatin architecture and epigenetic status of a gene are regulated by cytoplasmic components.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The phosphatidylinositol 3,5-bisphosphate (PI(3,5)P2)-dependent Tup1 conversion (PIPTC) regulates metabolic reprogramming from glycolysis to gluconeogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 12;288(28):20633-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.452813. Epub 2013 Jun 3. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23733183 Free PMC article.
-
Cti6, a PHD domain protein, bridges the Cyc8-Tup1 corepressor and the SAGA coactivator to overcome repression at GAL1.Mol Cell. 2002 Jun;9(6):1297-305. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00545-2. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12086626
-
The Cyc8-Tup1 complex inhibits transcription primarily by masking the activation domain of the recruiting protein.Genes Dev. 2011 Dec 1;25(23):2525-39. doi: 10.1101/gad.179275.111. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22156212 Free PMC article.
-
Turning genes off by Ssn6-Tup1: a conserved system of transcriptional repression in eukaryotes.Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Jul;25(7):325-30. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01592-9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000. PMID: 10871883 Review.
-
Phosphoinositide signaling during membrane transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Subcell Biochem. 2012;59:35-63. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-3015-1_2. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22374087 Review.
Cited by
-
Current progress on pathogenicity-related transcription factors in Fusarium oxysporum.Mol Plant Pathol. 2021 Jul;22(7):882-895. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13068. Epub 2021 May 9. Mol Plant Pathol. 2021. PMID: 33969616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sumoylation controls the timing of Tup1-mediated transcriptional deactivation.Nat Commun. 2015 Mar 13;6:6610. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7610. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25766875 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous mutations in CYC8 and MIG1 suppress the short chronological lifespan of budding yeast lacking SNF1/AMPK.Microb Cell. 2018 Feb 19;5(5):233-248. doi: 10.15698/mic2018.05.630. Microb Cell. 2018. PMID: 29796388 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of PIKfyve in multiple cellular pathways.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2022 Jun;76:102086. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2022.102086. Epub 2022 May 16. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35584589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Components of Golgi-to-vacuole trafficking are required for nitrogen- and TORC1-responsive regulation of the yeast GATA factors.Microbiologyopen. 2014 Jun;3(3):271-87. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.168. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Microbiologyopen. 2014. PMID: 24644271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballas N, Mandel G 2005. The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neuronal genes. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15: 500–506 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
