Pretransplant CSF-1 therapy expands recipient macrophages and ameliorates GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
- PMID: 21536742
- PMCID: PMC3092347
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20101709
Pretransplant CSF-1 therapy expands recipient macrophages and ameliorates GVHD after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation
Abstract
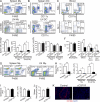
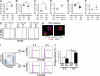
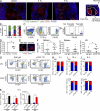
Acute graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) results from the attack of host tissues by donor allogeneic T cells and is the most serious limitation of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (allo-HCT). Host antigen-presenting cells are thought to control the priming of alloreactive T cells and the induction of acute GVHD after allo-HCT. However, whereas the role of host DC in GVHD has been established, the contribution of host macrophages to GVHD has not been clearly addressed. We show that, in contrast to DC, reducing of the host macrophage pool in recipient mice increased donor T cell expansion and aggravated GVHD mortality after allo-HCT. We also show that host macrophages that persist after allo-HCT engulf donor allogeneic T cells and inhibit their proliferation. Conversely, administration of the cytokine CSF-1 before transplant expanded the host macrophage pool, reduced donor T cell expansion, and improved GVHD morbidity and mortality after allo-HCT. This study establishes the unexpected key role of host macrophages in inhibiting GVHD and identifies CSF-1 as a potential prophylactic therapy to limit acute GVHD after allo-HCT in the clinic.
Figures
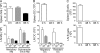




References
-
- Abe M., Cheng J., Qi J., Glaser R.M., Thall A.D., Sykes M., Yang Y.-G. 2002. Elimination of porcine hemopoietic cells by macrophages in mice. J. Immunol. 168:621–628 - PubMed
-
- Alyea E., Weller E., Schlossman R., Canning C., Webb I., Doss D., Mauch P., Marcus K., Fisher D., Freeman A., et al. 2001. T-cell—depleted allogeneic bone marrow transplantation followed by donor lymphocyte infusion in patients with multiple myeloma: induction of graft-versus-myeloma effect. Blood. 98:934–939 10.1182/blood.V98.4.934 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI071185/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI080884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI080884/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL086899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL097819/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA026504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL086899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA112100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA112100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA026504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL069438/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA032551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL116340/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI 071185/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- CA32551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA26504/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL69438/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

