Thrombospondin 1 inhibits inflammatory lymphangiogenesis by CD36 ligation on monocytes
- PMID: 21536744
- PMCID: PMC3092349
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20092277
Thrombospondin 1 inhibits inflammatory lymphangiogenesis by CD36 ligation on monocytes
Abstract
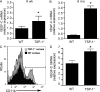
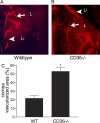
Lymphangiogenesis plays an important role in tumor metastasis and transplant outcome. Here, we show that thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), a multifunctional extracellular matrix protein and naturally occurring inhibitor of angiogenesis inhibits lymphangiogenesis in mice. Compared with wild-type mice, 6-mo-old TSP-1-deficient mice develop increased spontaneous corneal lymphangiogenesis. Similarly, in a model of inflammation-induced corneal neovascularization, young TSP-1-deficient mice develop exacerbated lymphangiogenesis, which can be reversed by topical application of recombinant human TSP-1. Such increased corneal lymphangiogenesis is also detected in mice lacking CD36, a receptor for TSP-1. In these mice, repopulation of corneal macrophages with predominantly WT mice via bone marrow reconstitution ameliorates their prolymphangiogenic phenotype. In vitro, exposure of WT macrophages to TSP-1 suppresses expression of lymphangiogenic factors vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and VEGF-D, but not of a primarily hemangiogenic factor VEGF-A. Inhibition of VEGF-C is not detected in the absence or blockade of CD36. These findings suggest that TSP-1, by ligating CD36 on monocytic cells, acts as an endogenous inhibitor of lymphangiogenesis.
Figures




References
-
- Albuquerque R.J., Hayashi T., Cho W.G., Kleinman M.E., Dridi S., Takeda A., Baffi J.Z., Yamada K., Kaneko H., Green M.G., et al. 2009. Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 is an essential endogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth. Nat. Med. 15:993–994 10.1038/nm.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

