Obligate biotrophy features unraveled by the genomic analysis of rust fungi
- PMID: 21536894
- PMCID: PMC3107277
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1019315108
Obligate biotrophy features unraveled by the genomic analysis of rust fungi
Abstract
Rust fungi are some of the most devastating pathogens of crop plants. They are obligate biotrophs, which extract nutrients only from living plant tissues and cannot grow apart from their hosts. Their lifestyle has slowed the dissection of molecular mechanisms underlying host invasion and avoidance or suppression of plant innate immunity. We sequenced the 101-Mb genome of Melampsora larici-populina, the causal agent of poplar leaf rust, and the 89-Mb genome of Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici, the causal agent of wheat and barley stem rust. We then compared the 16,399 predicted proteins of M. larici-populina with the 17,773 predicted proteins of P. graminis f. sp tritici. Genomic features related to their obligate biotrophic lifestyle include expanded lineage-specific gene families, a large repertoire of effector-like small secreted proteins, impaired nitrogen and sulfur assimilation pathways, and expanded families of amino acid and oligopeptide membrane transporters. The dramatic up-regulation of transcripts coding for small secreted proteins, secreted hydrolytic enzymes, and transporters in planta suggests that they play a role in host infection and nutrient acquisition. Some of these genomic hallmarks are mirrored in the genomes of other microbial eukaryotes that have independently evolved to infect plants, indicating convergent adaptation to a biotrophic existence inside plant cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
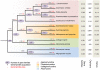
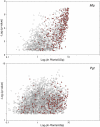
Comment in
-
Genomes of obligate plant pathogens reveal adaptations for obligate parasitism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 31;108(22):8921-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105802108. Epub 2011 May 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21576481 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Aime MC, et al. An overview of the higher level classification of Pucciniomycotina based on combined analyses of nuclear large and small subunit rDNA sequences. Mycologia. 2006;98:896–905. - PubMed
-
- Cummins GB, Hiratsuka Y. Illustrated Genera of Rust Fungi. 3rd Ed. St. Paul: APS Press; 2004.
-
- Leonard KJ, Szabo LJ. Stem rust of small grains and grasses caused by Puccinia graminis. Mol Plant Pathol. 2005;6:99–111. - PubMed
-
- Stokstad E. Plant pathology. Deadly wheat fungus threatens world's breadbaskets. Science. 2007;315:1786–1787. - PubMed
-
- Rubin EM. Genomics of cellulosic biofuels. Nature. 2008;454:841–845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

