Thyroxine is a potential endogenous antagonist of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) activity
- PMID: 21536912
- PMCID: PMC3100930
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1017624108
Thyroxine is a potential endogenous antagonist of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) activity
Abstract
Abnormally low plasma concentrations of thyroid hormones during sepsis often occur in the absence of thyroidal illness; however, the mechanisms involved in the "euthyroid sick syndrome" remain poorly understood. Here, we describe a previously unrecognized interaction between the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T(4)) and the proinflammatory cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), together with its clinical relevance in sepsis. We found that in both patients with severe sepsis, and our rodent model, low plasma T(4) concentrations were inversely correlated with plasma MIF concentrations. The MIF molecule contains a hydrophobic pocket that is important for many of its proinflammatory activities. Binding of L-T(4) (or its hormonally inert isomer D-T(4)) significantly, and dose-dependently, inhibited the catalytic activity of this pocket. Moreover, administration of exogenous D-T(4) significantly improved survival in mice with severe sepsis. To examine the specificity of the MIFT(4) interaction, wild-type and MIF knockout mice were subjected to the carrageenan-air pouch model of inflammation and then treated with D-T(4) or vehicle. D-T(4) significantly inhibited leukocyte infiltration in wild-type mice but not in MIF knockout mice, providing evidence that in vivo T(4) may influence MIF-mediated inflammatory responses via inhibition of its hydrophobic proinflammatory pocket. These findings demonstrate a new physiological role for T(4) as a natural inhibitor of MIF proinflammatory activity. The data may also, in part, explain the low plasma T(4) concentrations in critically ill, euthyroid patients and suggest that targeting the imbalance between MIF and T(4) may be beneficial in improving outcome from sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Y.A. is an inventor on a patent for the use of D-T4 in the treatment of sepsis.
Figures
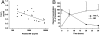



References
-
- Plikat K, et al. Frequency and outcome of patients with nonthyroidal illness syndrome in a medical intensive care unit. Metabolism. 2007;56:239–244. - PubMed
-
- Bello G, et al. Nonthyroidal illness syndrome and prolonged mechanical ventilation in patients admitted to the ICU. Chest. 2009;135:1448–1454. - PubMed
-
- Mebis L, van den Berghe G. The hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid axis in critical illness. Neth J Med. 2009;67:332–340. - PubMed
-
- Umpierrez GE. Euthyroid sick syndrome. South Med J. 2002;95:506–513. - PubMed
-
- Bernhagen J, et al. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993;365:756–759. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

