Protein binding: do we ever learn?
- PMID: 21537013
- PMCID: PMC3122431
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01433-10
Protein binding: do we ever learn?
Abstract
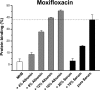
Although the influence of protein binding (PB) on antibacterial activity has been reported for many antibiotics and over many years, there is currently no standardization for pharmacodynamic models that account for the impact of protein binding of antimicrobial agents in vitro. This might explain the somewhat contradictory results obtained from different studies. Simple in vitro models which compare the MIC obtained in protein-free standard medium versus a protein-rich medium are prone to methodological pitfalls and may lead to flawed conclusions. Within in vitro test systems, a range of test conditions, including source of protein, concentration of the tested antibiotic, temperature, pH, electrolytes, and supplements may influence the impact of protein binding. As new antibiotics with a high degree of protein binding are in clinical development, attention and action directed toward the optimization and standardization of testing the impact of protein binding on the activity of antibiotics in vitro become even more urgent. In addition, the quantitative relationship between the effects of protein binding in vitro and in vivo needs to be established, since the physiological conditions differ. General recommendations for testing the impact of protein binding in vitro are suggested.
Figures
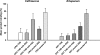
Similar articles
-
Protein binding of antimicrobials: methods for quantification and for investigation of its impact on bacterial killing.AAPS J. 2009 Mar;11(1):1-12. doi: 10.1208/s12248-008-9072-1. Epub 2009 Jan 1. AAPS J. 2009. PMID: 19117135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[In vitro MIC break point for appropriate clinical use of antibiotic].Jpn J Antibiot. 1993 Mar;46(3):205-21. Jpn J Antibiot. 1993. PMID: 8510318 Review. Japanese.
-
Impact of erythrocytes on bacterial growth and antimicrobial activity of selected antibiotics.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Mar;38(3):485-495. doi: 10.1007/s10096-018-03452-4. Epub 2019 Jan 28. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30687870 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of glucose added urine on the in vitro antimicrobial activity of various antibiotics.Indian J Med Res. 2008 Nov;128(5):663-5. Indian J Med Res. 2008. PMID: 19179689
-
[Simplified liquid nutrient media for controlling antibiotic activity, the spectrum of their antibacterial action and the sensitivity of microorganisms].Antibiotiki. 1977 Mar;22(3):216-9. Antibiotiki. 1977. PMID: 15506 Russian.
Cited by
-
A Simple, Fast, Low Cost, HPLC/UV Validated Method for Determination of Flutamide: Application to Protein Binding Studies.Adv Pharm Bull. 2016 Jun;6(2):251-6. doi: 10.15171/apb.2016.034. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016. PMID: 27478788 Free PMC article.
-
Defining the Active Fraction of Daptomycin against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Using a Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Approach.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 10;11(6):e0156131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156131. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27284923 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput 1,536-well fluorescence polarization assays for α(1)-acid glycoprotein and human serum albumin binding.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045594. Epub 2012 Sep 20. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029124 Free PMC article.
-
Plastic binding feature of polymyxins: the effect on MIC susceptibility measurements.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Aug 27;12:2649-2653. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S219130. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31695440 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Wearable Biosensors for the Continuous Monitoring of Biomarkers of Chronic Disease in Interstitial Fluid.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Jul 20;14(7):1452. doi: 10.3390/mi14071452. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37512763 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ackerman B. H., Taylor E. H., Olsen K. M., Abdel-Malak W., Pappas A. A. 1988. Vancomycin serum protein binding determination by ultrafiltration. Drug Intell. Clin. Pharm. 22:300–303 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad B., Parveen S., Khan R. H. 2006. Effect of albumin conformation on the binding of ciprofloxacin to human serum albumin: a novel approach directly assigning binding site. Biomacromolecules 7:1350–1356 - PubMed
-
- Allegaert K., et al. 2009. Cefazolin plasma protein binding saturability during pregnancy. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 31:25–28 - PubMed
-
- Ataullakhanov F. I., Kulikova E. V., Vitvitsky V. M. 1996. Reversible binding of anthracycline antibiotics to erythrocytes treated with glutaraldehyde. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 24(Part 3):241–244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

