Multiple implications of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in human cancer
- PMID: 21537480
- PMCID: PMC3083972
- DOI: 10.4331/wjbc.v1.i8.239
Multiple implications of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in human cancer
Abstract
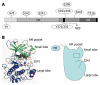
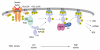
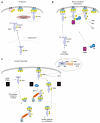
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) is a central mediator of cellular signaling between phosphoinositide-3 kinase and various intracellular serine/threonine kinases, including protein kinase B, p70 ribosomal S6 kinase, serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase, and protein kinase C. PDK1 activates members of the AGC family of protein kinases by phosphorylating serine/threonine residues in the activation loop. Here, we review the regulatory mechanisms of PDK1 and its roles in cancer. PDK1 is activated by autophosphorylation in the activation loop and other serine residues, as well as by phosphorylation of Tyr-9 and Tyr-373/376. Src appears to recognize PDK1 following tyrosine phosphorylation. The role of heat shock protein 90 in regulating PDK1 stability and PDK1-Src complex formation are also discussed. Furthermore, we summarize the subcellular distribution of PDK1. Finally, an important role for PDK1 in cancer chemotherapy is proposed. In conclusion, a better understanding of its molecular regulatory mechanisms in various signaling pathways will help to explain how PDK1 acts as an oncogenic kinase in various cancers, and will contribute to the development of novel cancer chemotherapies.
Keywords: 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1; Cancer therapy; Cell signaling; Oncogenic kinase; Protein kinase B.
Figures
Similar articles
-
3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 as an emerging target in the management of breast cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2013 Aug 23;5:271-80. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S35026. eCollection 2013. Cancer Manag Res. 2013. PMID: 24039447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 in activating AGC kinases defined in embryonic stem cells.Curr Biol. 2000 Apr 20;10(8):439-48. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00441-3. Curr Biol. 2000. PMID: 10801415
-
Identification of tyrosine phosphorylation sites on 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 and their role in regulating kinase activity.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 5;276(40):37459-71. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105916200. Epub 2001 Jul 31. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11481331
-
Regulation of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) by Src involves tyrosine phosphorylation of PDK1 and Src homology 2 domain binding.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 18;283(3):1480-1491. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706361200. Epub 2007 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18024423
-
PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Apr;15(2):161-70. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2003.12.022. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15209375 Review.
Cited by
-
PKCη/Rdx-driven phosphorylation of PDK1: a novel mechanism promoting cancer cell survival and permissiveness for parvovirus-induced lysis.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Mar 5;11(3):e1004703. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004703. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25742010 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic potential of microRNA-138 and its target mRNA PDK1 in sera for patients with non-small cell lung cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 Sep;31(9):129. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0129-y. Epub 2014 Jul 27. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25064732
-
Plant-derived cell-penetrating microprotein α-astratide aM1 targets Akt signaling and alleviates insulin resistance.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Sep 16;80(10):293. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04937-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37715850 Free PMC article.
-
The Cellular Prion Protein-ROCK Connection: Contribution to Neuronal Homeostasis and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Apr 12;15:660683. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.660683. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33912016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The anti-tumor NC1 domain of collagen XIX inhibits the FAK/ PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway through αvβ3 integrin interaction.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 12;7(2):1516-28. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6399. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26621838 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pearce LR, Komander D, Alessi DR. The nuts and bolts of AGC protein kinases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:9–22. - PubMed
-
- Mora A, Komander D, van Aalten DM, Alessi DR. PDK1, the master regulator of AGC kinase signal transduction. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004;15:161–170. - PubMed
-
- Stephens L, Anderson K, Stokoe D, Erdjument-Bromage H, Painter GF, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, McCormick F, Tempst P, et al. Protein kinase B kinases that mediate phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent activation of protein kinase B. Science. 1998;279:710–714. - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, Deak M, Casamayor A, Caudwell FB, Morrice N, Norman DG, Gaffney P, Reese CB, MacDougall CN, Harbison D, et al. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr Biol. 1997;7:776–789. - PubMed
-
- Stokoe D, Stephens LR, Copeland T, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Painter GF, Holmes AB, McCormick F, Hawkins PT. Dual role of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate in the activation of protein kinase B. Science. 1997;277:567–570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

