Rapid quantification of myocardial fibrosis: a new macro-based automated analysis
- PMID: 21538025
- PMCID: PMC3162624
- DOI: 10.1007/s13402-011-0035-7
Rapid quantification of myocardial fibrosis: a new macro-based automated analysis
Abstract
Background: Fibrosis is associated with various cardiac pathologies and dysfunction. Current quantification methods are time-consuming and laborious. We describe a semi-automated quantification technique for myocardial fibrosis and validated this using traditional methods.
Methods: Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) was induced in adult Wistar rats by subcutaneous monocrotaline (MCT) injection(40 mg/kg). Cryosections of myocardial tissue (5 μm) of PH rats (n = 9) and controls (n = 9) were stained using Picrosirius red and scanned with a digital microscopic MIRAX slide scanner. From these sections 21 images were taken randomly of each heart. Using ImageJ software a macro for automated image analysis of the amount of fibrosis was developed. For comparison, fibrosis was quantified using traditional polarisation microscopy. Both methods were correlated and validated against stereology as the gold standard. Furthermore, the method was tested in paraffin-embedded human tissues.
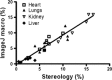
Results: Automated analysis showed a significant increase of fibrosis in PH hearts vs. control. Automated analysis correlated with traditional polarisation and stereology analysis (r(2) = 0.92 and r(2) = 0.95 respectively). In human heart, lungs, kidney, and liver, a similar correlation with stereology (r(2) = 0.91) was observed. Time required for automated analysis was 22% and 33% of the time needed for stereology and polarisation analysis respectively.
Conclusion: Automated quantification of fibrosis is feasible, objective, and time-efficient.
Figures

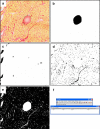

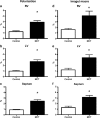
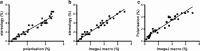
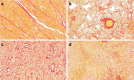
Corrected and republished from
-
Rapid quantification of myocardial fibrosis: A new macro-based automated analysis.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2010;33(5):257-69. doi: 10.3233/ACP-CLO-2010-0548. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2010. Corrected and republished in: Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2011 Aug;34(4):343-54. doi: 10.1007/s13402-011-0035-7. PMID: 20978317 Free PMC article. Corrected and republished.
References
-
- Brilla CG, Pick R, Tan LB, Janicki JS, Weber KT. Remodeling of the rat right and left ventricles in experimental hypertension. Circ Res. 1990;67:1355–1364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

