Lupus T cells switched on by DNA hypomethylation via microRNA?
- PMID: 21538310
- PMCID: PMC3201744
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30192
Lupus T cells switched on by DNA hypomethylation via microRNA?
Figures
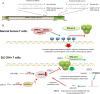
Comment on
-
MicroRNA-126 regulates DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells and contributes to systemic lupus erythematosus by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 May;63(5):1376-86. doi: 10.1002/art.30196. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21538319
References
-
- Zhao S, Wang Y, Liang Y, Zhao M, Long H, Ding S, et al. MicroRNA-126 regulates DNA methylation in CD4+ T cells and contributes to systemic lupus erythematosus by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 - PubMed
-
- Ballestar E, Esteller M, Richardson BC. The epigenetic face of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2006;176:7143–7. - PubMed
-
- Pan W, Zhu S, Yuan M, Cui H, Wang L, Luo X, et al. MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-148a contribute to DNA hypomethylation in lupus CD4+ T cells by directly and indirectly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. J Immunol. 2010;184:6773–81. - PubMed
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610. - PubMed
-
- Tang Y, Luo X, Cui H, Ni X, Yuan M, Guo Y, et al. MicroRNA-146A contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60:1065–75. - PubMed

