Interactions of halichondrin B and eribulin with tubulin
- PMID: 21539396
- PMCID: PMC3130535
- DOI: 10.1021/ci200077t
Interactions of halichondrin B and eribulin with tubulin
Abstract
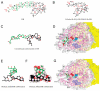
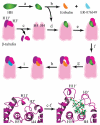
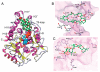
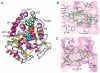
Compounds that modulate microtubule dynamics include highly effective anticancer drugs, leading to continuing efforts to identify new agents and improve the activity of established ones. Here, we demonstrate that [(3)H]-labeled halichondrin B (HB), a complex, sponge-derived natural product, is bound to and dissociated from tubulin rapidly at one binding site per αβ-heterodimer, with an apparent K(d) of 0.31 μM. We found no HB-induced aggregation of tubulin by high-performance liquid chromatography, even following column equilibration with HB. Binding of [(3)H]HB was competitively inhibited by a newly approved clinical agent, the truncated HB analogue eribulin (apparent K(i), 0.80 μM) and noncompetitively by dolastatin 10 and vincristine (apparent K(i)'s, 0.35 and 5.4 μM, respectively). Our earlier studies demonstrated that HB inhibits nucleotide exchange on β-tubulin, and this, together with the results presented here, indicated the HB site is located on β-tubulin. Using molecular dynamics simulations, we determined complementary conformations of HB and β-tubulin that delineated in atomic detail binding interactions of HB with only β-tubulin, with no involvement of the α-subunit in the binding interaction. Moreover, the HB model served as a template for an eribulin binding model that furthered our understanding of the properties of eribulin as a drug. Overall, these results established a mechanistic basis for the antimitotic activity of the halichondrin class of compounds.
Figures



References
-
- Bai R, Paull KD, Herald CL, Malspeis L, Pettit GR, Hamel E. Halichondrin B and homohalichondrin B, marine natural products binding in the vinca domain of tubulin: discovery of tubulin-based mechanism of action by analysis of differential cytotoxicity data. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:15882–15889. - PubMed
-
- Dabydeen DA, Burnett JC, Bai R, Verdier-Pinard P, Hickford SJH, Pettit GR, Blunt JW, Munro MHG, Gussio R, Hamel E. Comparison of the activities of the truncated halichondrin B analog NSC 707389 (E7389) with those of the parent compound and a proposed binding site on tubulin. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006;70:1866–1875. - PubMed
-
- Aicher TD, Buszek KR, Fang FG, Forsyth CJ, Jung SH, Kishi Y, Matelich MC, Scola PM, Spero DM, Yoon SK. Total synthesis of halichondrin B and norhalichondrin B. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992;114:3162–3164.
-
- Choi HW, Demeke D, Kang FA, Kishi Y, Nakajima K, Nowak P, Wan ZK, Xie CY. Synthetic studies on the marine natural product halichondrins. Pure Appl. Chem. 2003;75:1–17.
-
- Zheng W, Seletsky BM, Palme MH, Lydon PJ, Singer LA, Chase CE, Lemelin CA, Shen YC, Davis H, Tremblay L, Towle MJ, Salvato KA, Wels BF, Aalfs KK, Kishi Y, Littlefield BA, Yu MJ. Macrocyclic ketone analogues of halichondrin B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004;14:5551–5554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

