Conventional and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging findings of benign fibromatous paratesticular tumor: a case report
- PMID: 21539739
- PMCID: PMC3113326
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-5-169
Conventional and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging findings of benign fibromatous paratesticular tumor: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: The vast majority of paratesticular masses are benign. Magnetic resonance imaging of the scrotum may provide valuable information in the pre-operative work-up of scrotal masses, by allowing the precise localization of the lesion and helping in characterizing its nature. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging is an evolving technique that can be used to improve tissue characterization, when interpreted with the findings of conventional magnetic resonance sequences. We present the case of an adenomatoid tumor of the tunica albuginea, with abundant fibrosis evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging of the scrotum, including both conventional and diffusion-weighted sequences. To the best of our knowledge, there are very few reports in the English literature regarding the magnetic resonance imaging features of this rare benign paratesticular tumor and no report on the diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance findings. We discuss the value of magnetic resonance imaging in the pre-operative diagnosis of benign fibromatous paratesticular tumors and differential diagnosis.
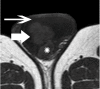
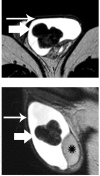
Case presentation: A 45-year-old Caucasian man was referred to us with a palpable left scrotal mass. Magnetic resonance imaging of his scrotum revealed the presence of a multilobular left paratesticular mass, mainly detected with very low signal intensity on T2-weighted images and restricted diffusion on apparent diffusion coefficient maps. These findings were suggestive of a fibrous component, and were confirmed on histology following lesion excision.
Conclusion: Magnetic resonance imaging of the scrotum, by using both conventional and diffusion-weighted sequences, could have a potential role in the evaluation of scrotal masses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance imaging findings of cellular angiofibroma of the tunica vaginalis of the testis: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Mar 31;10:71. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0861-3. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27029567 Free PMC article.
-
Sonographically indeterminate scrotal masses: how MRI helps in characterization.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018 Jul;24(4):225-236. doi: 10.5152/dir.2018.17400. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30091713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Left paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor on the single testis and contribution of imaging in therapeutic management, a case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Apr;105:108077. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108077. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36996707 Free PMC article.
-
Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor in young males presenting with histological features of IgG4-related disease: two case reports.J Med Case Rep. 2013 Sep 11;7:225. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-7-225. J Med Case Rep. 2013. PMID: 24025610 Free PMC article.
-
MRI of the scrotum: Recommendations of the ESUR Scrotal and Penile Imaging Working Group.Eur Radiol. 2018 Jan;28(1):31-43. doi: 10.1007/s00330-017-4944-3. Epub 2017 Jul 11. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 28698942 Review.
Cited by
-
MR Imaging Findings of Uterine Adenomatoid Tumors.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2024 Apr 1;23(2):127-135. doi: 10.2463/mrms.mp.2022-0067. Epub 2023 Jan 26. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 36697028 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging findings of cellular angiofibroma of the tunica vaginalis of the testis: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2016 Mar 31;10:71. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-0861-3. J Med Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27029567 Free PMC article.
-
Sonographically indeterminate scrotal masses: how MRI helps in characterization.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018 Jul;24(4):225-236. doi: 10.5152/dir.2018.17400. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30091713 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

