Interaction of enterocyte FABPs with phospholipid membranes: clues for specific physiological roles
- PMID: 21539932
- PMCID: PMC3143005
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2011.04.005
Interaction of enterocyte FABPs with phospholipid membranes: clues for specific physiological roles
Abstract
Intestinal and liver fatty acid binding proteins (IFABP and LFABP, respectively) are cytosolic soluble proteins with the capacity to bind and transport hydrophobic ligands between different sub-cellular compartments. Their functions are still not clear but they are supposed to be involved in lipid trafficking and metabolism, cell growth, and regulation of several other processes, like cell differentiation. Here we investigated the interaction of these proteins with different models of phospholipid membrane vesicles in order to achieve further insight into their specificity within the enterocyte. A combination of biophysical and biochemical techniques allowed us to determine affinities of these proteins to membranes, the way phospholipid composition and vesicle size and curvature modulate such interaction, as well as the effect of protein binding on the integrity of the membrane structure. We demonstrate here that, besides their apparently opposite ligand transfer mechanisms, both LFABP and IFABP are able to interact with phospholipid membranes, but the factors that modulate such interactions are different for each protein, further implying different roles for IFABP and LFABP in the intracellular context. These results contribute to the proposed central role of intestinal FABPs in the lipid traffic within enterocytes as well as in the regulation of more complex cellular processes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
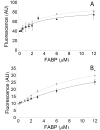

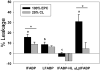


References
-
- Bass NM. Function and Regulation of Hepatic and Intestinal Fatty-Acid Binding Proteins. Chem Phys Lipids. 1985;38:95–114. - PubMed
-
- Glatz JFC, vanderVusse GJ. Cellular fatty acid-binding proteins: Their function and physiological significance. Prog Lipid Res. 1996;35:243–282. - PubMed
-
- Storch J, Corsico B. The emerging functions and mechanisms of mammalian fatty acid-binding proteins. Annu Rev Nutr. 2008;28:73–95. - PubMed
-
- Storch J, Thumser AEA. The fatty acid transport function of fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta-Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 2000;1486:28–44. - PubMed
-
- Storch J, Herr FM, Hsu KT, Kim HK, Liou HL, Smith ER. The role of membranes and intracellular binding proteins in cytoplasmic transport of hydrophobic molecules: Fatty acid-binding proteins. Comp Biochem Physiol Biochem Mol Biol. 1996;115:333–339.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

