Extra-adrenal glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids: evidence for local synthesis, regulation, and function
- PMID: 21540450
- PMCID: PMC3275156
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00100.2011
Extra-adrenal glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids: evidence for local synthesis, regulation, and function
Abstract
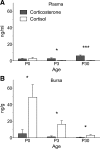
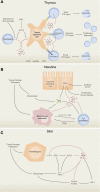
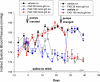
Glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids are steroid hormones classically thought to be secreted exclusively by the adrenal glands. However, recent evidence has shown that corticosteroids can also be locally synthesized in various other tissues, including primary lymphoid organs, intestine, skin, brain, and possibly heart. Evidence for local synthesis includes detection of steroidogenic enzymes and high local corticosteroid levels, even after adrenalectomy. Local synthesis creates high corticosteroid concentrations in extra-adrenal organs, sometimes much higher than circulating concentrations. Interestingly, local corticosteroid synthesis can be regulated via locally expressed mediators of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis or renin-angiotensin system (RAS). In some tissues (e.g., skin), these local control pathways might form miniature analogs of the pathways that regulate adrenal corticosteroid production. Locally synthesized glucocorticoids regulate activation of immune cells, while locally synthesized mineralocorticoids regulate blood volume and pressure. The physiological importance of extra-adrenal glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids has been shown, because inhibition of local synthesis has major effects even in adrenal-intact subjects. In sum, while adrenal secretion of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids into the blood coordinates multiple organ systems, local synthesis of corticosteroids results in high spatial specificity of steroid action. Taken together, studies of these five major organ systems challenge the conventional understanding of corticosteroid biosynthesis and function.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad N, Romero DG, Gomez-Sanchez EP, Gomez-Sanchez CE. Do human vascular endothelial cells produce aldosterone? Endocrinology 145: 3626–3629, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Atanasov AG, Leiser D, Roesselet C, Noti M, Corazza N, Schoonjans K, Brunner T. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of extra-adrenal glucocorticoid synthesis in murine intestinal epithelial cells. FASEB J 22: 4117–4125, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Batanero E, de Leeuw FE, Jansen GH, van Wichen DF, Huber J, Schuurman HJ. The neural and neuro-endocrine component of the human thymus. II. Hormone immunoreactivity. Brain Behav Immun 6: 249–264, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Beyenburg S, Watzka M, Clusmann H, Blumcke I, Bidlingmaier F, Elger CE, Stoffel-Wagner B. Messenger RNA of steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21) is expressed in the human hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 308: 111–114, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

