Fabrication of porous scaffolds with a controllable microstructure and mechanical properties by porogen fusion technique
- PMID: 21541032
- PMCID: PMC3083679
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms12020890
Fabrication of porous scaffolds with a controllable microstructure and mechanical properties by porogen fusion technique
Abstract
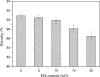
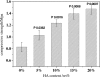
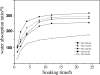
Macroporous scaffolds with controllable pore structure and mechanical properties were fabricated by a porogen fusion technique. Biodegradable material poly (d, l-lactide) (PDLLA) was used as the scaffold matrix. The effects of porogen size, PDLLA concentration and hydroxyapatite (HA) content on the scaffold morphology, porosity and mechanical properties were investigated. High porosity (90% and above) and highly interconnected structures were easily obtained and the pore size could be adjusted by varying the porogen size. With the increasing porogen size and PDLLA concentration, the porosity of scaffolds decreases, while its mechanical properties increase. The introduction of HA greatly increases the impact on pore structure, mechanical properties and water absorption ability of scaffolds, while it has comparatively little influence on its porosity under low HA contents. These results show that by adjusting processing parameters, scaffolds could afford a controllable pore size, exhibit suitable pore structure and high porosity, as well as good mechanical properties, and may serve as an excellent substrate for bone tissue engineering.
Keywords: composite scaffolds; mechanical property; porogen fusion technique; tissue engineering.
Figures








References
-
- Hutmacher DW. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2529–2543. - PubMed
-
- Temenoff JS, Mikos AG. Tissue engineering for regeneration of articular cartilage. Biomaterials. 2000;21:431–440. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Zhang M. Synthesis and characterization of macroporous chitosan/calcium phosphate composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001;55:304–312. - PubMed
-
- Rizzi SC, Heath DJ, Coombes AGA, Bock N, Textor M, Downes S. Biodegradable polymer/hydroxyapatite composites: Surface analysis and initial attachment of human osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001;55:475–486. - PubMed
-
- Wang M. Developing bioactive composite materials for tissue replacement. Biomaterials. 2003;24:2133–2151. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

