Fixed-time schedule effects in combination with response-dependent schedules
- PMID: 21541131
- PMCID: PMC3050458
- DOI: 10.1901/jaba.2011.44-163
Fixed-time schedule effects in combination with response-dependent schedules
Abstract
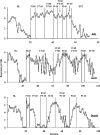
We evaluated the effects of fixed-interval (FI), fixed-time (FT), and conjoint (combined) FI FT reinforcement schedules on the responding of 3 adults who had been diagnosed with schizophrenia. Responding on vocational tasks decreased for 2 of 3 participants under FT alone relative to FI alone. Responding under FI FT resulted in response persistence for 2 of 3 participants. Results have implications for the maintenance of desirable behavior, as well as for situations in which FT treatment has been implemented for problem behavior and problem behavior is nevertheless reinforced by caregivers.
Keywords: conjoint schedules; noncontingent reinforcement; schizophrenia; time-based schedules; vocational skills.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human responding on random-interval schedules of response-cost punishment: the role of reduced reinforcement density.J Exp Anal Behav. 2010 Jan;93(1):5-26. doi: 10.1901/jeab.2010.93-5. J Exp Anal Behav. 2010. PMID: 20676265 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of noncontingent reinforcement on an arbitrary response in domestic dogs (Canis lupus familiaris).Behav Processes. 2022 Nov;203:104770. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2022.104770. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Behav Processes. 2022. PMID: 36283576
-
Variable-time reinforcement schedules in the treatment of socially maintained problem behavior.J Appl Behav Anal. 2000 Winter;33(4):545-57. doi: 10.1901/jaba.2000.33-545. J Appl Behav Anal. 2000. PMID: 11214030 Free PMC article.
-
"The stone which the builders rejected...": Delay of reinforcement and response rate on fixed-interval and related schedules.Behav Processes. 2006 Feb 28;71(2-3):77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.beproc.2005.08.006. Epub 2005 Nov 22. Behav Processes. 2006. PMID: 16307848 Review.
-
Applying Standards of Effectiveness to Noncontingent Reinforcement: A Systematic Literature Review.Behav Modif. 2021 Jul;45(4):619-640. doi: 10.1177/0145445519865073. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Behav Modif. 2021. PMID: 31452379
References
-
- Catania A.C. Learning (4th ed.) Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall; 1998.
-
- Nevin J.A. Choice and behavior momentum. In: O'Donohue W, editor. Learning and behavior therapy. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn and Bacon; 1998. pp. 230–251. (Ed.)
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources