Neurocytoma of the cerebellum
- PMID: 21541206
- PMCID: PMC3086174
- DOI: 10.4103/2152-7806.78246
Neurocytoma of the cerebellum
Abstract
Background: Neurocytomas are benign central nervous system tumor composed of small cells with characteristics of neuronal differentiation; they are usually located in the supratentorial periventricular region, in close relation to the septum pellucidum and the foramen of Monro.
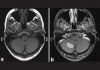
Case description: Herein we report a rare case of a neurocytoma located in the cerebellar hemisphere. To date there are only four such reported cases.
Conclusion: Neurocytomas should be considered in the differential diagnosis of mass lesions in the cerebellum.
Keywords: Cerebellar hemisphere; neurocytoma; posterior fossa.
Figures

References
-
- Alcock J, Lowe J, England T, Bath P, Sottile V. Expression of Sox1, Sox2 and Sox9 is maintained in adult human cerebellar cortex. Neurosci Lett. 2009;450:114–6. - PubMed
-
- Alcock J, Sottile V. Dynamic distribution and stem cell characteristics of Sox1-expressing cells in the cerebellar cortex. Cell Res. 2009;19:1324–33. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa MD, Balsitis M, Jaspan T, Lowe J. Intraventricular neurocytoma: A clinical and pathological study of three cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1990;26:1045–54. - PubMed
-
- Brat DJ, Scheithauer BW, Eberhart CG, Burger PC. Extraventricular neurocytomas: Pathologic features and clinical outcome. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;10:1252–60. - PubMed
-
- Brandis A, Heyer R, Hori A, Walter GF. Cerebellar neurocytoma in an infant: An important differential diagnosis from cerebellar neuroblastoma and medulloblastoma? Neuropediatrics. 1997;28:235–8. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

