Glucose and fatty acids synergize to promote B-cell apoptosis through activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β independent of JNK activation
- PMID: 21541314
- PMCID: PMC3082528
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018146
Glucose and fatty acids synergize to promote B-cell apoptosis through activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β independent of JNK activation
Abstract
Background: The combination of elevated glucose and free-fatty acids (FFA), prevalent in diabetes, has been suggested to be a major contributor to pancreatic β-cell death. This study examines the synergistic effects of glucose and FFA on β-cell apoptosis and the molecular mechanisms involved. Mouse insulinoma cells and primary islets were treated with palmitate at increasing glucose and effects on apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and insulin receptor substrate (IRS) signaling were examined.
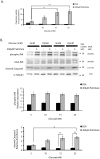
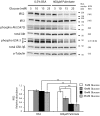
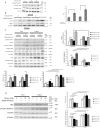
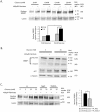
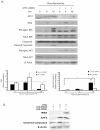
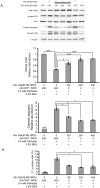
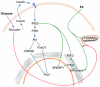
Principal findings: Increasing glucose (5-25 mM) with palmitate (400 µM) had synergistic effects on apoptosis. Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) activation peaked at the lowest glucose concentration, in contrast to a progressive reduction in IRS2 protein and impairment of insulin receptor substrate signaling. A synergistic effect was observed on activation of ER stress markers, along with recruitment of SREBP1 to the nucleus. These findings were confirmed in primary islets. The above effects associated with an increase in glycogen synthase kinase 3β (Gsk3β) activity and were reversed along with apoptosis by an adenovirus expressing a kinase dead Gsk3β.
Conclusions/significance: Glucose in the presence of FFA results in synergistic effects on ER stress, impaired insulin receptor substrate signaling and Gsk3β activation. The data support the importance of controlling both hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia in the management of Type 2 diabetes, and identify pancreatic islet β-cell Gsk3β as a potential therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, et al. Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52:102–110. - PubMed
-
- Weir GC, Laybutt DR, Kaneto H, Bonner-Weir S, Sharma A. Beta-cell adaptation and decompensation during the progression of diabetes. Diabetes. 2001;50(Suppl 1):S154–159. - PubMed
-
- Unger RH. [Maurice Derot Prize 2001. The liporegulator system and disease]. Journ Annu Diabetol Hotel Dieu. 2001:129–143. - PubMed
-
- Donath MY, Halban PA. Decreased beta-cell mass in diabetes: significance, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Diabetologia. 2004;47:581–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P60 DK20579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK016746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK064938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK33301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033301/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK16746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK016746/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK64938/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055267/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

