Cardioprotective effect of nicorandil, a mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener, prolongs survival in HSPB5 R120G transgenic mice
- PMID: 21541347
- PMCID: PMC3081834
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018922
Cardioprotective effect of nicorandil, a mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener, prolongs survival in HSPB5 R120G transgenic mice
Abstract
Background: Transgenic (TG) mice with overexpression of an arg120gly (R120G) missense mutation in HSPB5 display desmin-related cardiomyopathy, which is characterized by formation of aggresomes. It is also known that progressive mitochondrial abnormalities and apoptotic cell death occur in the hearts of R120G TG mice. The role of mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in disease progression, however, remains uncertain.
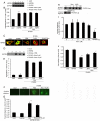
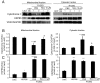
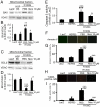
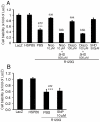
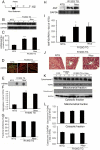
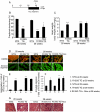
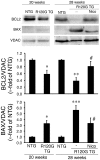
Methods and results: Mitochondrial abnormalities and apoptotic cell death induced by overexpression of HSPB5 R120G were analyzed in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Overexpression of mutant HSPB5 led to development of aggresomes with a concomitant reduction in cell viability in the myocytes. Overexpression of mutant HSPB5 induced a reduction in the cytochrome c level in the mitochondrial fraction and a corresponding increase in the cytoplasmic fraction in the myocytes. Down-regulation of BCL2 and up-regulation of BAX were detected in the myocytes expressing the mutant HSPB5. Concomitant with mitochondrial abnormality, the activation of caspase-3 and increased apoptotic cell death was observed. Cell viability was dose-dependently recovered in myocytes overexpressing HSPB5 R120G by treatment with nicorandil a mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener. Nicorandil treatment also inhibited the increase in BAX, the decrease in BCL2, activation of caspase-3 and apoptotic cell death by mutant HSPB5. To confirm the results of the in-vitro study, we analyzed the effect of nicorandil in HSPB5 R120G TG mice. Nicorandil treatment appeared to reduce mitochondrial impairment and apoptotic cell death and prolonged survival in HSPB5 R120G TG mice.
Conclusions: Nicorandil may prolong survival in HSPB5 R120G TG mice by protecting against mitochondrial impairments.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
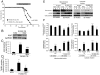
References
-
- IONA Study Group. Determinants of coronary events in patients with stable angina: results from the impact of nicorandil in angina study. Am Heart J. 2005;150:689. - PubMed
-
- Das B, Sarkar C. Mitochondrial K ATP channel activation is important in the antiarrhythmic and cardioprotective effects of non-hypotensive doses of nicorandil and cromakalim during ischemia/reperfusion: a study in an intact anesthetized rabbit model. Pharmacol Res. 2003;47:447–461. - PubMed
-
- IONA Study Group. Effect of nicorandil on coronary events in patients with stable angina: the Impact Of Nicorandil in Angina (IONA) randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1269–1275. - PubMed
-
- Nishikawa S, Tatsumi T, Shiraishi J, Matsunaga S, Takeda M, et al. Nicorandil regulates Bcl-2 family proteins and protects cardiac myocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2006;40:510–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

