Paeoniflorin suppresses the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in endotoxin-treated human monocytic cells
- PMID: 21542832
- PMCID: PMC3188904
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01464.x
Paeoniflorin suppresses the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in endotoxin-treated human monocytic cells
Abstract
Background and purpose: Paeoniflorin (PF) has ameliorative effects on learning and memory impairment and cerebral ischaemia in rats and has protective effects against the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. The neuroprotective effects of PF are most probably derived from its anti-inflammatory property. Abnormally high levels of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) have been found to be associated with a wide range of inflammatory and immune responses. Here we studied whether PF regulates the levels of ICAM-1 elevated in LPS-activated differentiated human monocytic U937 cells and TNF-α-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs).
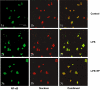
Experimental approach: mRNA levels were evaluated by RT-PCR. Protein levels were evaluated by Western blot analysis. An immunofluorescence technique was used to estimate NF-κB translocation, and NF-κB binding to nuclear DNA was determined by EMSA.
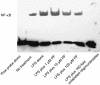
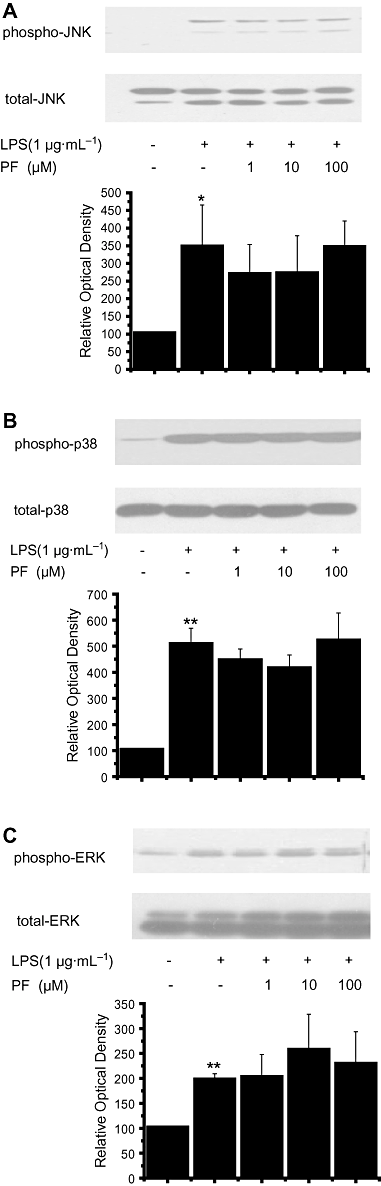
Key results: PF inhibited ICAM-1 expression elevated in LPS-induced U937 cells and TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs. Although previous reports showed that PF's action is mediated by activating adenosine A₁ receptors, application of a selective adenosine A₁ receptor antagonist did not change the inhibitory effect of PF in our experiments. To elucidate the underlying mechanisms of the effect of PF, we studied its effect on signalling pathways upstream of ICAM-1 expression. PF suppressed the activation of the NF-κB pathway, which regulates the expression of ICAM-1. The TLR4 and MAPK pathways were shown not to be involved in the effects of PF in these cells.
Conclusions and implications: PF inhibits ICAM-1 expression in LPS-treated U937 cells and TNF-α-stimulated HUVECs by suppressing the activation of the NF-κB pathway.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures





References
-
- Bernot D, Peiretti F, Canault M, Juhan-Vague I, Nalbone G. Upregulation of TNF-alpha-induced ICAM-1 surface expression by adenylate cyclase-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 2005;202:434–441. - PubMed
-
- Cotran RS, Mayadas-Norton T. Endothelial adhesion molecules in health and disease. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1998;46:164–170. - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald KA, Rowe DC, Golenbock DT. Endotoxin recognition and signal transduction by the TLR4/MD2-complex. Microbes Infect. 2004;6:1361–1367. - PubMed
-
- Ip WK, Wong CK, Lam CW. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human eosinophilic leukaemia EoL-1 cells is mediated by the activation of nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003;33:241–248. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

