Assembly of the Caulobacter cell division machine
- PMID: 21542856
- PMCID: PMC3707389
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07677.x
Assembly of the Caulobacter cell division machine
Abstract
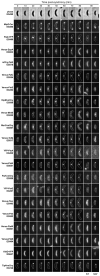
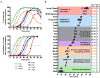
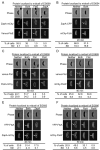
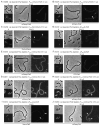
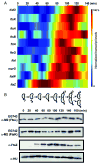
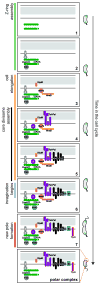
Cytokinesis in Gram-negative bacteria is mediated by a multiprotein machine (the divisome) that invaginates and remodels the inner membrane, peptidoglycan and outer membrane. Understanding the order of divisome assembly would inform models of the interactions among its components and their respective functions. We leveraged the ability to isolate synchronous populations of Caulobacter crescentus cells to investigate assembly of the divisome and place the arrival of each component into functional context. Additionally, we investigated the genetic dependence of localization among divisome proteins and the cell cycle regulation of their transcript and protein levels to gain insight into the control mechanisms underlying their assembly. Our results revealed a picture of divisome assembly with unprecedented temporal resolution. Specifically, we observed (i) initial establishment of the division site, (ii) recruitment of early FtsZ-binding proteins, (iii) arrival of proteins involved in peptidoglycan remodelling, (iv) arrival of FtsA, (v) assembly of core divisome components, (vi) initiation of envelope invagination, (vii) recruitment of polar markers and cytoplasmic compartmentalization and (viii) cell separation. Our analysis revealed differences in divisome assembly among Caulobacter and other bacteria that establish a framework for identifying aspects of bacterial cytokinesis that are widely conserved from those that are more variable.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

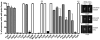

References
-
- Aaron M, Charbon G, Lam H, Schwarz H, Vollmer W, Jacobs-Wagner C. The tubulin homologue FtsZ contributes to cell elongation by guiding cell wall precursor synthesis in Caulobacter crescentus. Mol Microbiol. 2007;64:938–952. - PubMed
-
- Aarsman ME, Piette A, Fraipont C, Vinkenvleugel TM, Nguyen-Disteche M, den Blaauwen T. Maturation of the Escherichia coli divisome occurs in two steps. Mol Microbiol. 2005;55:1631–1645. - PubMed
-
- Addinall SG, Cao C, Lutkenhaus J. FtsN, a late recruit to the septum in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1997;25:303–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

