The two faces of ToxR: activator of ompU, co-regulator of toxT in Vibrio cholerae
- PMID: 21542860
- PMCID: PMC3124598
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07681.x
The two faces of ToxR: activator of ompU, co-regulator of toxT in Vibrio cholerae
Abstract
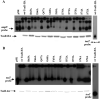
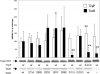
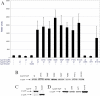
ToxR of Vibrio cholerae directly activates the ompU promoter, but requires a second activator, TcpP to activate the toxT promoter. ompU encodes a porin, while toxT encodes the transcription factor, ToxT, which activates V. cholerae virulence genes including cholera toxin and the toxin co-regulated pilus. Using an ompU-sacB transcriptional fusion, toxR mutant alleles were identified that encode ToxR molecules defective for ompU promoter activation. Many toxR mutants defective for ompU activation affected residues involved in DNA binding. Mutants defective for ompU activation were also tested for activation of the toxT promoter. ToxR-F69A and ToxR-V71A, both in the α-loop of ToxR, were preferentially defective for ompU activation, with ToxR-V71A nearly completely defective. Six mutants from the ompU-sacB selection showed more dramatic defects in toxT activation than ompU activation. All but one of the affected residues map to the wing domain of the winged helix-turn-helix of ToxR. Some ToxR mutants preferentially affecting toxT activation had partial DNA-binding defects, and one mutant, ToxR-P101L, had altered interactions with TcpP. These data suggest that while certain residues in the α-loop of ToxR are utilized to activate the ompU promoter, the wing domain of ToxR contributes to both promoter binding and ToxR/TcpP interaction facilitating toxT activation.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




References
-
- Blanco AG, Sola M, Gomis-Ruth FX, Coll M. Tandem DNA Recognition by PhoB, a Two-Component Signal Transduction Transcriptional Activator. Structure. 2002;10:701–713. - PubMed
-
- Carroll PA, Tashima KT, Rogers MB, DiRita VJ, Calderwood SB. Phase variation in tcpH modulates expression of the ToxR regulon in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 1997;25:1099–1111. - PubMed
-
- Champion GA, Neely MN, Brennan MA, DiRita VJ. A branch in the ToxR regulatory cascade of Vibrio cholerae revealed by characterization of toxT mutant strains. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:323–331. - PubMed
-
- Crawford JA, Kaper JB, DiRita VJ. Analysis of ToxR-dependent transcription activation of ompU, the gene encoding a major envelope protein in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 1998;29:235–246. - PubMed
-
- Crawford JA, Krukonis ES, DiRita VJ. Membrane localization of the ToxR winged-helix domain is required for TcpP-mediated virulence gene activation in Vibrio cholerae. Mol Microbiol. 2003;47:1459–1473. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

