The role of the central nervous system in the generation and maintenance of chronic pain in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia
- PMID: 21542893
- PMCID: PMC3132050
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3306
The role of the central nervous system in the generation and maintenance of chronic pain in rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis and fibromyalgia
Abstract
Pain is a key component of most rheumatologic diseases. In fibromyalgia, the importance of central nervous system pain mechanisms (for example, loss of descending analgesic activity and central sensitization) is well documented. A few studies have also noted alterations in central pain processing in osteoarthritis, and some data, including the observation of widespread pain sensitivity, suggest that central pain-processing defects may alter the pain response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. When central pain is identified, different classes of analgesics (for example, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, α2δ ligands) may be more effective than drugs that treat peripheral or nociceptive pain (for example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opioids).
Figures
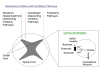
References
-
- Borenstein D, Altman R, Bello A, Chatham W, Clauw DJ, Crofford LJ, Croft J, Hassett A, Kozin F, Pisetsky D, Richardson J, Schanberg LE, Starz T, Witter J. Report of the American College of Rheumatology Pain Management Task Force. Arthritis Care Res. 2010;62:590–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

