Lack of neuroprotection in the absence of P2X7 receptors in toxin-induced animal models of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 21542899
- PMCID: PMC3113297
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-28
Lack of neuroprotection in the absence of P2X7 receptors in toxin-induced animal models of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
Background: Previous studies indicate a role of P2X7 receptors in processes that lead to neuronal death. The main objective of our study was to examine whether genetic deletion or pharmacological blockade of P2X7 receptors influenced dopaminergic cell death in various models of Parkinson's disease (PD).
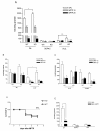
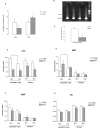
Results: mRNA encoding P2X7 and P2X4 receptors was up-regulated after treatment of PC12 cells with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). P2X7 antagonists protected against MPTP and rotenone induced toxicity in the LDH assay, but failed to protect after rotenone treatment in the MTT assay in PC12 cells and in primary midbrain culture. In vivo MPTP and in vitro rotenone pretreatments increased the mRNA expression of P2X7 receptors in the striatum and substantia nigra of wild-type mice. Basal mRNA expression of P2X4 receptors was higher in P2X7 knockout mice and was further up-regulated by MPTP treatment. Genetic deletion or pharmacological inhibition of P2X7 receptors did not change survival rate or depletion of striatal endogenous dopamine (DA) content after in vivo MPTP or in vitro rotenone treatment. However, depletion of norepinephrine was significant after MPTP treatment only in P2X7 knockout mice. The basal ATP content was higher in the substantia nigra of wild-type mice, but the ADP level was lower. Rotenone treatment elicited a similar reduction in ATP content in the substantia nigra of both genotypes, whereas reduction of ATP was more pronounced after rotenone treatment in striatal slices of P2X7 deficient mice. Although the endogenous amino acid content remained unchanged, the level of the endocannabinoid, 2-AG, was elevated by rotenone in the striatum of wild-type mice, an effect that was absent in mice deficient in P2X7 receptors.
Conclusions: We conclude that P2X7 receptor deficiency or inhibition does not support the survival of dopaminergic neurons in an in vivo or in vitro models of PD.
Figures



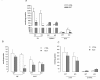

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

